Selection of a circuit breaker for power

The choice of protective circuit breakers is made not only during the installation of a new electrical network, but also during the modernization of the electrical panel, as well as when additional powerful devices are included in the circuit that increase the load to such a level that the old emergency shutdown devices cannot cope with. And in this article we will talk about how to correctly select the machine in terms of power, what should be taken into account during this process and what are its features.
Failure to understand the importance of this task can lead to very serious problems. After all, users often do not bother themselves, making the choice of a circuit breaker in terms of power, and take the first available device in the store, using one of two principles - "cheaper" or "more powerful". Such an approach, associated with the inability or unwillingness to calculate the total power of devices connected to the power grid, and in accordance with it to choose a circuit breaker, often becomes the reason for the failure of expensive equipment in case of a short circuit or even a fire.
Content
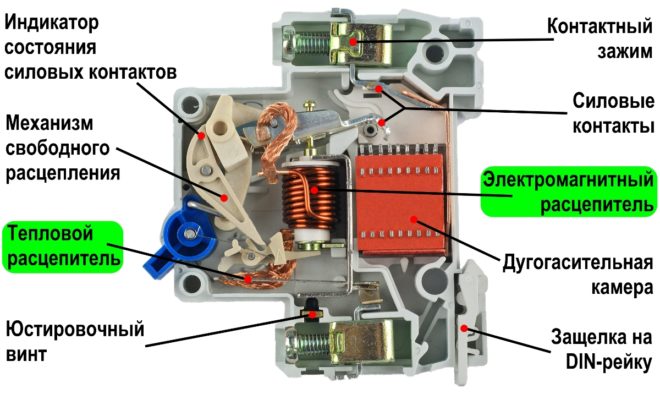
What are circuit breakers for and how do they work?
Modern AB have two degrees of protection: thermal and electromagnetic. This allows you to protect the line from damage as a result of prolonged excess of the flowing current of the rated value, as well as short circuit.
The main element of the thermal release is a two-metal plate, which is called bimetallic. If it is exposed to a current of increased power for a sufficiently long time, it becomes flexible and, acting on the tripping element, triggers the machine.
The presence of an electromagnetic release determines the breaking capacity of the circuit breaker when the circuit is exposed to short-circuit overcurrents, which it cannot withstand.
An electromagnetic release is a solenoid with a core, which, when a high power current passes through it, instantly shifts towards the tripping element, turning off the protective device and de-energizing the network.
This allows the wire and devices to be protected from the flow of electrons, the value of which is much higher than that calculated for a cable of a specific cross-section.
Why is the cable mismatch with the network load dangerous?
The correct selection of a power protection circuit breaker is a very important task. An incorrectly selected device will not protect the line from a sudden increase in current strength.

But it is equally important to choose the right wiring cable cross-section. Otherwise, if the total power exceeds the nominal value that the conductor can withstand, this will lead to a significant increase in the temperature of the latter. As a result, the insulating layer will begin to melt, which can lead to a fire.
In order to more clearly imagine what the inconsistency of the wiring cross-section of the total power of the devices connected to the network threatens, consider such an example.
New owners, having bought an apartment in an old house, install several modern household appliances in it, giving a total load on the circuit equal to 5 kW. The current equivalent in this case will be about 23 A. In accordance with this, a 25 A circuit breaker is included in the circuit. It would seem that the choice of the machine in terms of power was made correctly, and the network is ready for operation. But some time after turning on the appliances, smoke appears in the house with a characteristic smell of burnt insulation, and after a while a flame appears.In this case, the circuit breaker will not disconnect the network from the power supply - after all, the current rating does not exceed the permissible one.
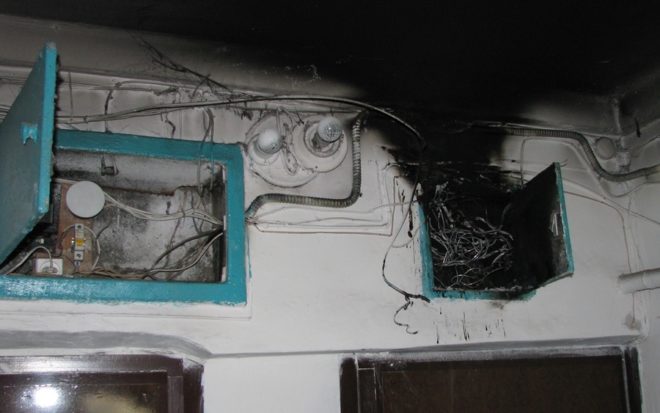

If the owner is not nearby at this moment, the molten insulation will cause a short circuit after a while, which will finally trigger the machine, but the flame from the wiring may already spread throughout the house.
The reason is that, although the calculation of the machine for power was done correctly, the wiring cable with a cross section of 1.5 mm² was designed for 19 A and could not withstand the existing load.
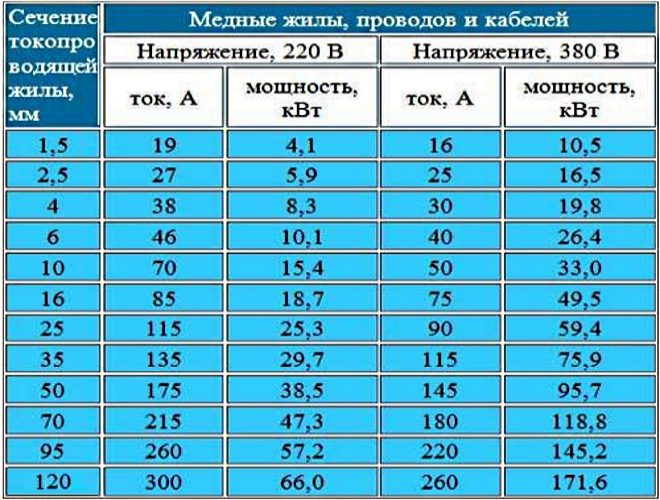
So that you do not have to take up the calculator and independently calculate the cross-section of the electrical wiring using the formulas, we present a typical table in which it is easy to find the desired value.
Weak link protection
So, we made sure that the calculation of the circuit breaker should be made based not only on the total power of the devices included in the circuit (regardless of their number), but also on the cross-section of the wires. If this indicator is not the same along the electric line, then we select the section with the smallest section and calculate the machine based on this value.
The requirements of the PUE state that the selected circuit breaker must provide protection for the weakest section of the electrical circuit, or have a current rating that will correspond to a similar parameter for the installations included in the network. This also means that for the connection, wires must be used whose cross-section will be able to withstand the total power of the connected devices.
How the selection of the wire cross-section and the rating of the circuit breaker is performed - in the following video:
If the negligent owner ignores this rule, then in the event of an emergency due to insufficient protection of the weakest section of the wiring, he should not blame the selected device and scold the manufacturer - only he himself will be the culprit of the situation.
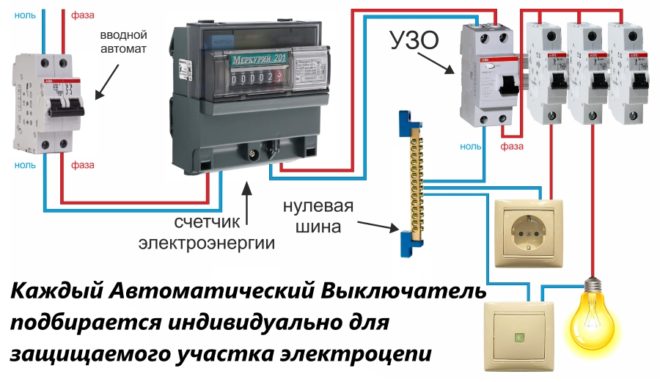
How to calculate the rating of a circuit breaker?
Let's say that we have taken into account all of the above and have selected a new cable that meets modern requirements and has the desired cross-section. Now the electrical wiring is guaranteed to withstand the load from the included household appliances, even if there are a lot of them. Now we go directly to the selection of the circuit breaker at the current rating. We recall the school physics course and determine the estimated load current by substituting the corresponding values in the formula: I = P / U.
Here I is the value of the rated current, P is the total power of the installations included in the circuit (taking into account all consumers of electricity, including light bulbs), and U is the mains voltage.
To simplify the choice of a circuit breaker and save you from having to take on a calculator, we present a table that shows the AB ratings that are included in single-phase and three-phase networks, and the corresponding total load power.
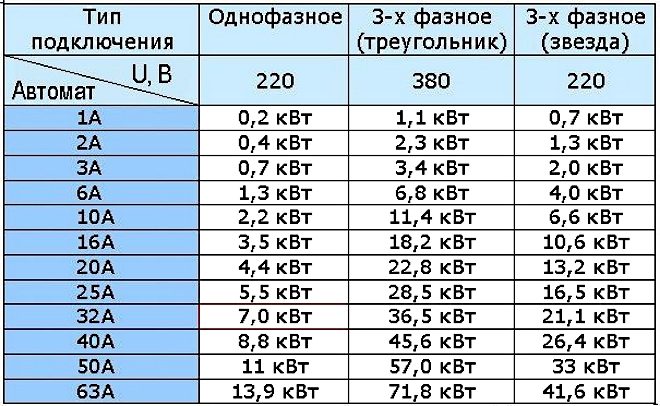
This table will make it easy to determine how many kilowatts of load correspond to which rated current of the protective device. As we can see, a 25 Ampere machine in a network with a single-phase connection and a voltage of 220 V corresponds to a power of 5.5 kW, for a 32 Amp AV in a similar network - 7.0 kW (in the table this value is highlighted in red). At the same time, for an electrical network with a three-phase "delta" connection and a rated voltage of 380 V, a 10 Ampere machine corresponds to a total load power of 11.4 kW.
Clearly about the selection of circuit breakers in the video:
Conclusion
In the presented material, we talked about what the electrical circuit protection devices are for and how they work. In addition, given the information provided and the tabular data provided, you will not be faced with the question of how to choose a circuit breaker.