Types of circuit breakers - what are the machines

Circuit breakers are devices whose task is to protect an electric line from the effects of a powerful current that can cause overheating of the cable with further melting of the insulating layer and fire. An increase in current strength can be caused by too much load, which occurs when the total power of the devices exceeds the value that the cable can withstand in its cross section - in this case, the machine does not turn off immediately, but after the wire heats up to a certain level. With a short circuit, the current increases many times over a fraction of a second, and the device immediately reacts to it, instantly stopping the supply of electricity to the circuit. In this material we will tell you what types of circuit breakers are and their characteristics.
Content
Circuit breakers: classification and differences
In addition to residual current circuit breakers, which are not used individually, there are 3 types of circuit breakers. They work with loads of different sizes and differ in their design. These include:
- Modular AB. These devices are installed in household networks in which currents of small magnitude flow. Usually have 1 or 2 poles and a width in multiples of 1.75 cm.

- Cast switches. They are designed to operate in industrial networks with currents up to 1 kA. Made in a cast case, which is why they got their name.
- Air electric machines. These devices can be 3 or 4 poles and can handle currents up to 6.3 kA. Used in electrical circuits with high power installations.
There is another type of circuit breakers for protecting the electrical network - differential. We do not consider them separately, since such devices are conventional circuit breakers, which include an RCD.
Release types
The releases are the main working components of AB. Their task is to break the circuit when the permissible current value is exceeded, thereby stopping the supply of electricity to it. There are two main types of these devices, which differ from each other in terms of the release principle:
- Electromagnetic.
- Thermal.
Electromagnetic-type releases provide almost instantaneous operation of the circuit breaker and de-energize the circuit section when an overcurrent short circuit occurs in it.

They are a coil (solenoid) with a core that is drawn inward under the influence of a large current and causes the tripping element to operate.
The main part of the thermal release is a bimetallic plate. When a current that exceeds the rated value of the protective device passes through the machine, the plate begins to heat up and, bending to the side, touches the disconnecting element, which is triggered and de-energizes the circuit. The tripping time of the thermal release depends on the magnitude of the overload current passing through the plate.
Some modern devices are equipped as a supplement with undervoltage (zero) releases. They perform the function of switching off the AB when the voltage falls below the limit value corresponding to the technical data of the device. There are also distance releases, with the help of which you can not only turn off, but also turn on the AB, even without going to the switchboard.
The presence of these options significantly increases the cost of the device.
Number of poles
As already mentioned, the network circuit breaker has poles - from one to four.

It is not difficult to choose a device for a circuit according to their number, it is enough just to know where different types of AB are used:
- Single-pole networks are installed to protect lines that include sockets and lighting fixtures. They are mounted on a phase conductor without capturing a neutral conductor.
- The two-pole must be included in the circuit to which household appliances with a sufficiently high power are connected (boilers, washing machines, electric stoves).
- Three-pole networks are installed in semi-industrial scale networks, to which devices such as borehole pumps or car workshop equipment can be connected.
- Four-pole AB allow you to protect electrical wiring with four cables from short circuit and overload.
The use of machines of different polarity is in the following video:
Characteristics of circuit breakers
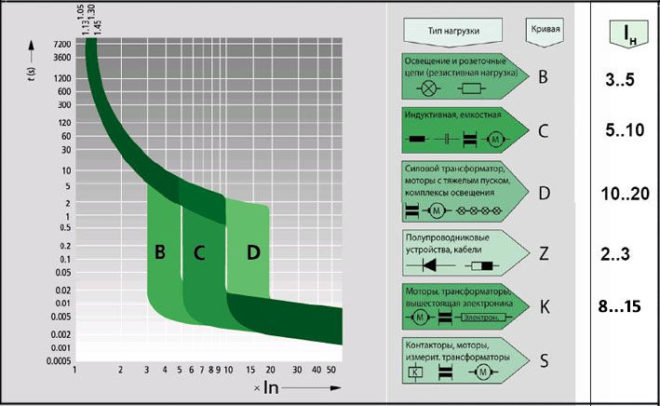
There is another classification of machines - according to their characteristics. This indicator indicates the degree of sensitivity of the protective device to exceeding the rated current. The corresponding marking will show how quickly the device will react in the event of an increase in current. Some types of AB work instantly, while others will take a certain amount of time.
There is the following marking of devices according to their sensitivity:
- A. Breakers of this type are the most sensitive and react instantly to increased load. They are practically not installed in household networks, protecting with their help circuits in which high-precision equipment is included.
- B. These circuit breakers operate when the current rises with a slight delay. Usually they are included in the line with expensive household appliances (LCD TVs, computers, and others).
- C. These devices are the most common in household networks. Their disconnection does not occur immediately after the increase in the current strength, but after a while, which makes it possible to normalize it with a slight drop.
- D. The sensitivity of these devices to increasing current is the lowest of all the types listed. They are most often installed in shields at the approach of the line to the building. They provide a safety net for the apartment machines, and if they do not work for some reason, they turn off the general network.

Features of the selection of machines
Some people think that the most reliable circuit breaker is the one that can handle the highest current, which means that it is he who can provide the maximum circuit protection. Based on this logic, an air-type machine can be connected to any network, and all problems will be solved. However, this is not at all the case.
To protect circuits with different parameters, it is necessary to install devices with appropriate capabilities.
Mistakes in the selection of AB are fraught with unpleasant consequences. If you connect a protective device designed for high power to a regular household circuit, then it will not de-energize the circuit, even when the current value significantly exceeds that that the cable can withstand. The insulating layer will heat up, then begin to melt, but the shutdown will not occur. The fact is that the current strength, which is destructive for the cable, will not exceed the nominal AB, and the device will "count" that there was no emergency. Only when the molten insulation causes a short circuit will the machine turn off, but by that time a fire may have already begun.
Here is a table that shows the ratings of the machines for various power grids.
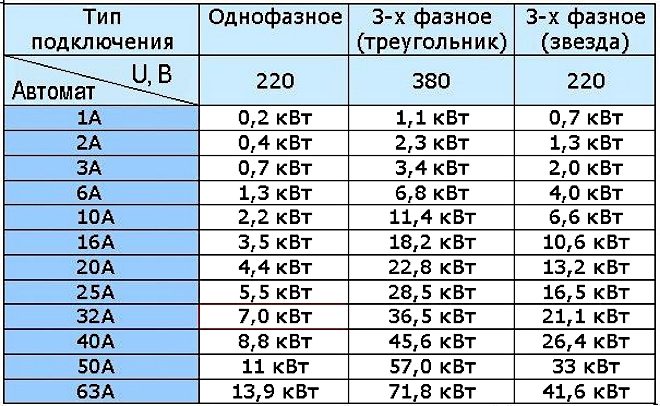
If the device is designed for less power than that which the line can withstand and which the connected devices have, the circuit will not be able to work normally. When the equipment is turned on, the AB will constantly knock out, and ultimately, under the influence of high currents, it will fail due to "stuck" contacts.
Clearly about the types of circuit breakers in the video:
Conclusion
The circuit breaker, the characteristics and types of which we have considered in this article, is a very important device that protects the electric line from damage by high currents. Operation of networks not protected by machines is prohibited by the Electrical Installation Rules. The most important thing is to choose the right type of AB, which is suitable for a particular network.