What is a dimmer and how does it work

For some time now, among the concepts of household electrical engineering, the word dimmer has been increasingly heard. What is this device? For what purposes is it intended? Maybe another whim? Or something really necessary in everyday life? There are a lot of questions, we will try to give detailed answers to all of them.
Content
Purpose
The word "dimmer" comes from the English "dim", which literally means "dim" in Russian. But the Russians themselves often call the dimmer a dimmer, because it is an electronic device with which you can change the electrical power (that is, adjust it up or down).

Most often, using such a device, the lighting load is controlled. The dimmer is designed to change the brightness of the light emitted by LED lamps, incandescent and halogen lamps.
 The simplest example of a dimmer is a variable resistor (or rheostat). Back in the 19th century, the German physicist Johann Poggendorf invented this device so that it could be used to regulate the voltage and current in an electrical circuit by increasing or decreasing resistance. A rheostat is a resistance-adjustable device and a conductive element. The resistance can change stepwise and smoothly. To obtain a low brightness of the light, it is necessary to reduce the voltage. But the resistance and current strength will be large, which will lead to strong heating of the device. So such a regulator is completely unprofitable, it will work with low efficiency.
The simplest example of a dimmer is a variable resistor (or rheostat). Back in the 19th century, the German physicist Johann Poggendorf invented this device so that it could be used to regulate the voltage and current in an electrical circuit by increasing or decreasing resistance. A rheostat is a resistance-adjustable device and a conductive element. The resistance can change stepwise and smoothly. To obtain a low brightness of the light, it is necessary to reduce the voltage. But the resistance and current strength will be large, which will lead to strong heating of the device. So such a regulator is completely unprofitable, it will work with low efficiency.
Autotransformers can also be used as a dimmer. Their use is due to their high efficiency; practically undistorted voltage with the required frequency of 50 Hz will be output throughout the entire adjustable range. But autotransformers are quite large, they weigh a lot, and considerable mechanical efforts are required to control them. In addition, such a device is expensive.
Electronic dimmer - this option is the most profitable from an economic point of view. It is compact and has a slightly different operating principle. Let's talk about it in more detail.
Application
What is a dimmer is more or less clear. Voltage is applied to the lamp, we change its level and thus adjust the brightness of the lamp. Now a few words about when and where this device is used.

Agree, quite often situations arise when a decrease in the brightness of light is required:
- often the flow of lighting must be reduced before going to bed in the bedroom;
- some design rooms require a change in the light pattern;
- sometimes the lighting in the premises is switched to the so-called standby mode in order to reduce energy consumption.
In industrial and domestic premises, LED lamps are tuned for different consumption modes. At the same time, optimal lighting is selected and due to this, decent energy savings are achieved.
As for design ideas, it has now become fashionable in large living rooms or hall rooms to use secondary highlighting of individual areas. The secondary lighting is thought out to the smallest detail, and with the help of dimmers you can increase the lighting and focus on some interior details (a picture on the wall, a beautiful vase installed in a niche, etc.) first plan.
Dimmable LED lamps allow you to get a colorful effect during some kind of concert, advertising or special events.
The dimmer is very handy for home celebrations. When guests are seated at the table, bright lighting is required, and during dancing, you can dim it. It is especially convenient and beneficial to use such a device during a romantic dinner or a date, when it is not necessary for the lamp to burn at full power.
And these are just some of the general examples. Surely, everyone has their own way of using dimmers. So this thing is necessary, convenient and cost-effective, you can install it at home and advise your friends.
Device and principle of operation
And now, as they say, let's look at the dimmer from the inside. What is this device, and what elements does it consist of? What is its principle of operation based on?
All modern electronic dimmers have a key (it can also be called a switch or switch) as the main element in their design, which is controlled by semiconductor transistor, triac or thyristor devices. Most devices do not output a sinusoidal signal at the output; the electronic switch cuts off the sections of the sinusoid.
To make it clearer for you, a current flows in the electrical network, which has a sinusoidal shape. To change the brightness, a cut-off sine wave must be fed to the lamp. The bi-directional thyristor cuts off the leading or trailing edge of the AC sine wave, thereby reducing the voltage supplying the lamp.
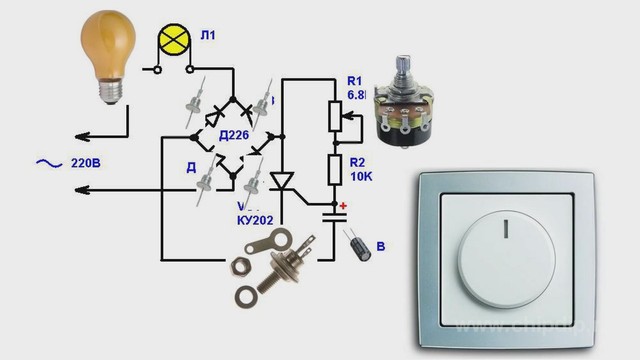
Depending on which front of the sine wave is cut off, the adjustable method differs:
- leading edge adjustment;
- trailing edge adjustment.
Both of these methods are used to control different lamps:
- Dimming of LED and halogen lamps is carried out using electronic transformers, while trailing edge control is applied.
- Compact fluorescent and LED lamps with a voltage of 220 V, as well as low voltage lamps, are regulated by means of electromagnetic transformers and using the leading edge method.
Both of these methods are suitable for incandescent lamps.
The design of the dimmers also includes protection against short circuit and overheating.
Since dimmers are capable of generating electromagnetic interference, a choke or inductive-capacitive filters are connected in series to the circuit to reduce their level.
For more information on a typical dimmer circuit, see this video:
Advantages and disadvantages
The first dimmers were mechanically controlled and had only one function - to change the brightness of the lamp.

The modern regulator has a number of other functions:
- Automatic switching on and off.
- It can be controlled remotely via radio channel, voice command, acoustic change (noise or pop), infrared channel.
- The touch-sensitive dimmer allows you to smoothly turn on and off the lamp. Due to this, it is possible to avoid sudden surges of current through the lamps, as a result of which the latter often burn out.
- Dimmers simulate presence. This is a particularly interesting feature that will help scare off "intruders" from your home when no one is home. A special program is set, according to which the dimmer automatically turns on and off the light in different rooms. The illusion is created that the owners are at home.
Like any technical device, a dimmer cannot be one hundred percent universal, it has its drawbacks:
- causes electromagnetic interference;
- the output voltage has a non-linear dependence on the value of the resistance of the resistor in the electronic dimmer circuit;
- fluorescent lamps cannot work from it, as well as lamps that light up through control gear;
- the output voltage of electronic dimmers has a non-sinusoidal shape, therefore it is not recommended to connect step-down transformers to it;
- low efficiency when working with incandescent lamps.
What dimmers are there?
According to the method of adjustment, there is a touch dimmer, mechanical, acoustic and remote.

Let's start with the simplest ones - mechanical. If we consider the type of performance, then the following types of dimmers can be distinguished:
- Modular. They control lighting in public places (stairwells, corridors, entrances). This type of device is mounted in a switchboard; direct adjustment is carried out by a push-button or one-button switch.
- Monoblock. It is installed to break the phase of the circuit, which goes to the lighting load, and acts as a switch.
- The block version is when the dimmer is mounted together with a switch (like a socket-switch unit).

Most often, monoblock dimmers are used in everyday life, which differ in the way of control:
- Turning. This dimmer has a knob, it rotates. If you set it to the left extreme position, then the lighting is turned off. If you gradually turn the knob to the right, the brightness of the lamp will increase.
- Key. This device is very similar in appearance to a conventional two-button switch. In this case, using one key, the lamp is switched on or off, and the second is used to adjust the lighting power (by holding the button).
- Swivel-push. The principle of operation is the same as that of the rotary device, only to turn on the lighting, the handle is slightly recessed.

The touch-sensitive dimmer is very popular now, it has a beautiful appearance, looks harmonious in any interior (especially in high-tech style). Adjustment is carried out by touching the touch buttons.
The most convenient are dimmers with remote control. This is well deserved, because using the remote control, you can adjust the brightness of the lighting device from anywhere in the room.

Acoustic dimmers are most often used when planning a "smart home", where the lighting can be controlled by voice commands or hand claps.
Dimmers can be divided according to the type of lamps they regulate:
- The simplest devices are used for incandescent and halogen lamps, which operate on a voltage of 220 V. Everything is simple here - the voltage changes, and the glow power of the filament is regulated.
- The circuit for 12 V or 24 V halogen lamps must be with a step-down transformer. When this is not possible, then choose a regulator for the type of transformer used (they have a special marking - C for electronic, RL for winding).
- LED lamps require dimmers with pulse frequency modulation.
Energy saving and fluorescent lamps are difficult to regulate. Experts generally do not recommend doing this. If you really need to control such bulbs, then include an electronic starter in the dimmer circuit.
For more information on dimming different types of lamps, see this video:
Well, we made an attempt to get acquainted with such a dimmer as a dimmer. We hope that now you more or less understand what it is and what the principle of operation is. Regarding the connection diagrams - dimmers are installed in the circuit either instead of the switch, or in series with it. By the way, if you are good friends with electronics from the first grade, then making a dimmer with your own hands will not be difficult for you.



