Why does the energy-saving lamp blink when the backlit switch is off

Currently, outdated and low-efficiency incandescent lamps are being replaced with energy-saving and LED ones. Thanks to their advantages, they are firmly entrenched in the lighting market. But they also have disadvantages, which we will talk about in this article, and also answer the question often asked by many consumers: why does the energy-saving lamp blink when the switch is off.
Content
The reason for the blinking of the turned off energy-saving lamp
Let's look at the physical causes of short-term flashes of disconnected lamps. To do this, we will explain the device and the principle of operation of energy-saving lamps, and then LED lamps.
Energy-saving lamp device
An energy-saving lamp consists of a gas-filled glass tube that emits light. To power it, a special starting circuit is used on electronic keys (electronic ballast). Such circuits operate exclusively on constant voltage. For its formation, a mains voltage rectifier and a filter consisting of a capacitor of a sufficiently large capacity and a choke are used.
It is this capacitor that is the reason for the flickering of the off lamp. It is known that a capacitor is an energy storage device. As the charge increases, the voltage on its plates increases. When its value exceeds the threshold for operation of the electronic key, the lamp starts up, accompanied by a glow. The energy stored in the capacitor is quickly consumed. That is why the glow is only in the form of flashes.
LED lamp device
The LED lamp contains a substrate on which the LEDs themselves are soldered (usually connected in several series circuits). They are powered by a special voltage converter, which includes a rectifier and a capacitive filter (made on a capacitor). No choke is required to power the LEDs.
Since LED lamps do not have a special electronic key, the glow can occur constantly as the energy stored in the capacitor is consumed. Therefore, such lamps, as a rule, do not blink, but only glow dimly.
The reason for charging the filter capacitor is the small current flowing in the circuit of the switched off lamp. Two reasons contribute to its appearance:
- Illuminated switches.
- Errors in wiring.
Let's take a closer look at each of the reasons.
Application of illuminated switches
A conventional backlit switch and an LED lamp do not always work together correctly, since the backlight circuit can only be designed to connect incandescent lamps. The principle of operation of such a switch is shown in the figure below.
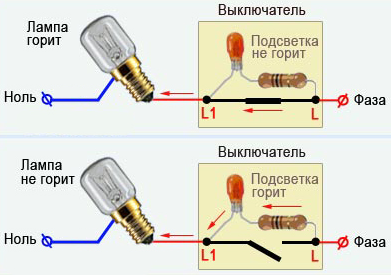
When using energy-saving and LED lamps, a small current flows through the backlight circuit, which charges the filter capacitor in the lamp. This current is enough for the switch backlight to function, but not enough for normal lamp operation. This process leads to blinking or faint glow.
Wiring errors
The same phenomenon described above occurs when:
- wrong connection of lamps;
- violation of the integrity of the insulation of wires;
- large capacity of wires in relation to the metal structures of the building.
If the luminaires are connected by mistake, the switch breaks not the phase, but the neutral wire of the supply network. In this case, the current flows through the phase wire, the lamp (charging the filter capacitor) and through the capacitance of the neutral wire on the metal structure.
If the integrity of the insulation of the wires is violated, a leakage current occurs, which can be closed directly to the metal structure, neutral wire or other wires. In this case, there is a danger of fire or electrical injury.
With a large capacity of the wires in relation to the grounded parts of the building, a small current also occurs. This phenomenon is due to the wrong choice of wires for wiring. For example, using a shielded wire.
Flicker-free methods
If you have LED or energy saving lights and backlit switches, there are three ways to eliminate flicker. The easiest way is to turn off the backlight. This can be done by disassembling the switch. In some models, you need to remove a separate backlight module, in others, you need to cut the wires going to this module. However, in this case, the meaning of using such switches is lost - after all, they will no longer be visible in the dark.
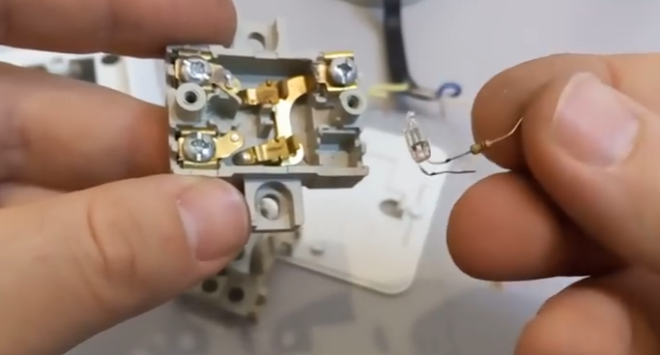
The second method is also quite simple: turning on a conventional incandescent lamp in parallel with an energy-saving one. Thus, the filament will be connected to the terminals of the filter capacitor, discharging it and preventing further charging. In operating mode, it does not affect the operation of the energy-saving lamp, since the operating current is much higher than the backlight and leakage current. The main disadvantage of this method is the complete absence of energy savings and the sense of purchasing energy-saving lamps.

This drawback can be corrected by connecting a conventional resistor instead of an incandescent lamp in parallel with an energy-saving one. The advantage of this method will remain, but the disadvantage will practically disappear. Let us dwell in more detail on the choice of a resistor and the features of its installation.
In order for a large current not to flow through the resistor during operation of the lamp, its resistance must be at least 50 kOhm. The lower the current, the less it heats up. Better even put a 75 or 100 kΩ resistor, whichever is easier to find. Its rated power must be at least 2 W (if a 100 kΩ resistor is used, it is allowed to use 1 W). MLT resistors work well.


The third method is the most difficult. It involves reworking the lighting of the switches. For this, the backlight output connected to the phase wire is left, and the second output is disconnected and connected to the neutral wire. The main disadvantage of this method is the need to lay a neutral wire to the switch, as well as the complexity of implementation (in some switches, the backlight module is printed on the board, its alteration consists in removing the contact and soldering an additional wire). In this case, the backlight in the switch is constantly on.
If energy-saving and LED lamps blink due to errors in wiring, then all of the above methods will not solve this problem (they can only create the appearance of a solution). In this case, the wiring must be redone, since its operation is dangerous.
Examples of connecting a resistor in parallel with a lamp
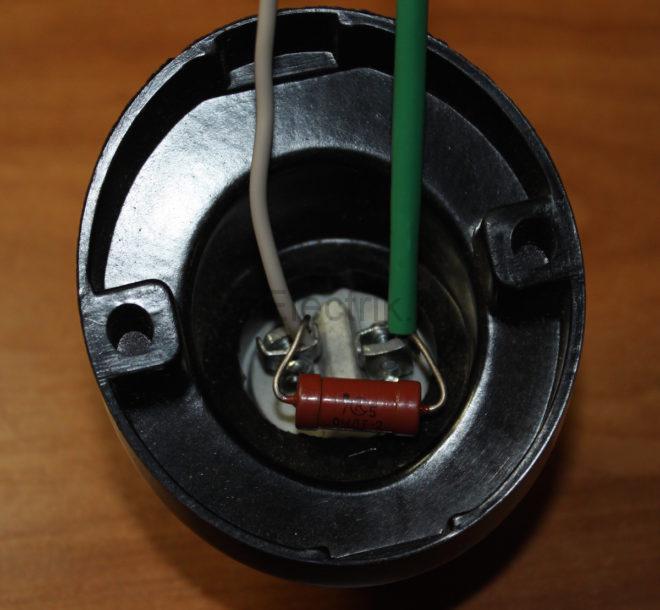
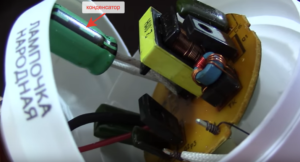
The photo below shows the option of connecting a resistor in the lamp holder. Its leads are clamped into terminal blocks for supply wires.
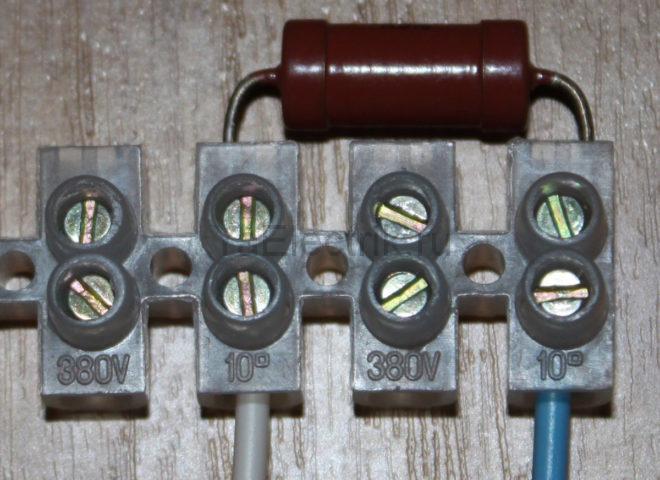
However, not all cartridges will fit this resistor. In this case, it must be installed in a junction box. Below is a photo of such a connection.
Note that the connection of the resistor in the junction box is much more reliable than in the socket, since there is enough space in it to install the terminal block. If there is still not enough space, you can place it directly in the chandelier, if its design allows. In this case, the resistor is in the same compartment as the wire connections. In this case, you need to take care of its reliable insulation, especially if the parts of the chandelier are metal.
Detailed video instruction on shunting an energy-saving lamp
How NOT to deal with flickering
It is believed that LED strips and lamps based on them blink after being turned off due to the fact that they are connected to low-power power supplies. This opinion is erroneous. In this case, the lamps will flicker only during operation. Therefore, it is important to choose a power supply unit with the required power or more powerful. If, after turning off, the LED strip flickers, then in parallel to it you need to connect a resistor with a resistance of 10 to 22 kOhm and a power of at least 0.5 W.
Conclusion
In this article, we looked at the question of why an LED or energy-saving lamp blinks or glows dimly when the switch is off. In conclusion, it should be noted that a common cause of lamp flickering is poor quality. In this case, unfortunately, you will not be able to fix the problem with your own hands and you will have to replace the light bulb with a product from another, perhaps better known, manufacturer.