Heat shrinkage for wires - purpose, types and sizes
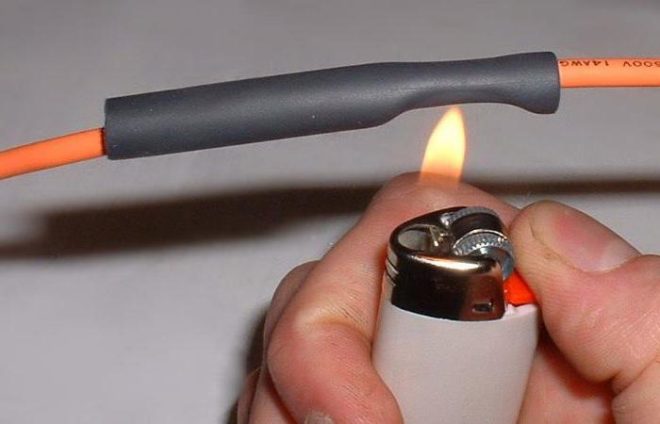

Heat-shrinkable materials have a fairly high electrical resistance, which is why they are widely used in electrical engineering. These materials on the market of electrical goods can be called new, but quite promising, due to the fact that they have excellent operational properties. The most widespread among them is the heat-shrinkable tube. Under the influence of high temperature, it contracts, and it does this only in the transverse direction, that is, the diameter decreases, but the length does not change at all.
What are these pipes? What properties and parameters do they have? What are they made of and how are they used correctly? We will try to answer all the questions.
Content
How are these tubes made?
For the production of heat-shrinkable parts, high or low pressure polyethylene is used. Polyethylene blanks should have such a geometric shape that the part will take in the future after thermal shrinkage. These blanks are subjected to modification, that is, they are exposed to a chemical or radiation method.

At the moment when the impact occurs, the process of elimination of hydrogen atoms from linear molecules begins in the polymer material. In this case, the molecules seem to be stitched together, and a completely different network structure is obtained, similar to rubber. A polymer material of such a structure additionally acquires such characteristic qualities as water resistance, elasticity and electrical insulating properties.
Then the polymer parts are heated to a temperature equal to the melting point of the starting material. During heating, the polymers will become elastic and soft, but since they have undergone a modification procedure, they will not melt. Parts in this hot state can be compressed or stretched, in general, given the necessary shape and size. Then they are cooled to room temperature. The resulting polymer parts will have a shape memory effect, that is, when exposed to heat (heating), they will take on their original geometric appearance.
What are heat-shrinkable products made of?

Thermotubes, in addition to polyethylene, are also made from the following polymeric materials:
- synthetic fluorinated rubber (fluoroelastomer);
- polymers of the polyolefin group;
- polyvinyl chloride;
- polyvinylidene;
- polytetrafluoroethylene (teflon);
- polyethylene terephthalate (polyester).
The temperature operating range of heat-shrinkable products also depends on the material (the gap is huge: from -60 to +260 degrees).
Basic requirements and properties

A heat-shrinkable tube made of polymer materials has unique properties:
- Resistant to high temperatures.
- Do not try to stretch it, it has a strength of at least 15 MPa.
- Resistance to acids, alkalis and other oil products.
- Withstands operating voltage up to 1000 V.
- Elastic.
- Easily deformed.
- Non-toxic.
- Not flammable.
- It has the ability to hermetically crimp objects with a complex embossed surface, which provides mechanical protection and electrical insulation.
- Simple enough installation that does not require special knowledge and skills.
- Low cost.
Application area
The heat-shrinkable tube has received the greatest application as a substitute for traditional electrical tape for electrical work.It is used as the main component of heat-shrinkable cable sleeves. With its help, you can restore the damaged insulation layer of the wires.

Often, a heat-shrinkable tube is used as a corrosion protection, with which conveyor rollers and rollers are rubberized.
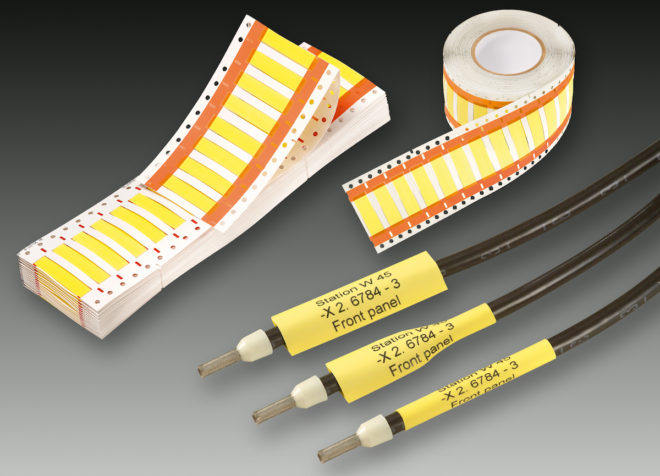
The use of such a heat-shrinkable tube is not limited only to insulating properties, it can be used to mark the cores of a cable or wire, which facilitates the further work and operation of the conductors. In this case, take tubes of different colors or with letter designations.
How to mark wires with a heat-shrinkable tube, see this video:
Such a polymer product is widely used in the chemical, oil refining and aviation industries, in radio engineering, automotive and telecommunications. The tubes are used to protect fuel and hydraulic systems from external mechanical influences.
Varieties
The types of heat shrinkable tubes depend on their design and installation principle.
Adhesive
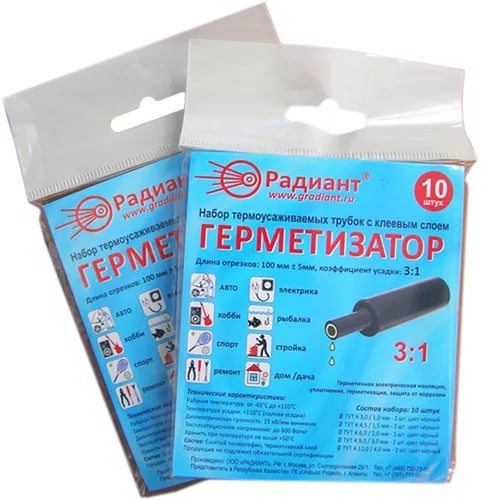

Glue heat shrinkage for wires has become widespread. In their design, a distinctive feature is the inner adhesive layer, due to which, at the time of thermal exposure, a more reliable sealing is obtained. Thanks to the glue, the tube tightens the junction of the wires, which almost ideally protects against moisture. The shrinkage factor for such tubes is more than 300%.
Thick-walled
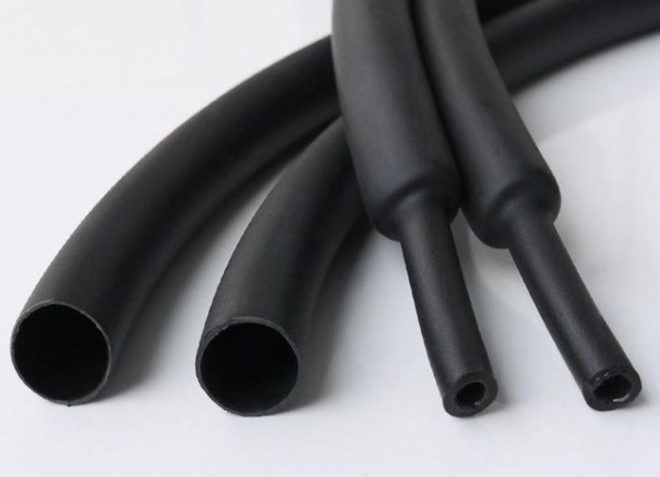

Due to the low cost and ease of installation, thick-walled tubes are also widely used. They are made from polyolefins. These products are produced in two types, some of them are capable of suppressing combustion, others do not have this ability. In the first version, non-combustible substances are used for manufacturing, and if an open fire does not fall on such a tube during combustion, it gradually dies out on its own. Such tubes have found application in industries with a high explosion hazard and in the military industry.
Special
These tubes are used when additional properties are required. For example, products that can withstand an operating voltage of over 1000 V are used in high-voltage electrical networks. They produce tubes of a fluorescent type, in the daytime they accumulate light, and at night they emit it. This option is widely used in rooms with low illumination. There are corrugated tubes, they cover the handles of power tools.
Specifications and parameters
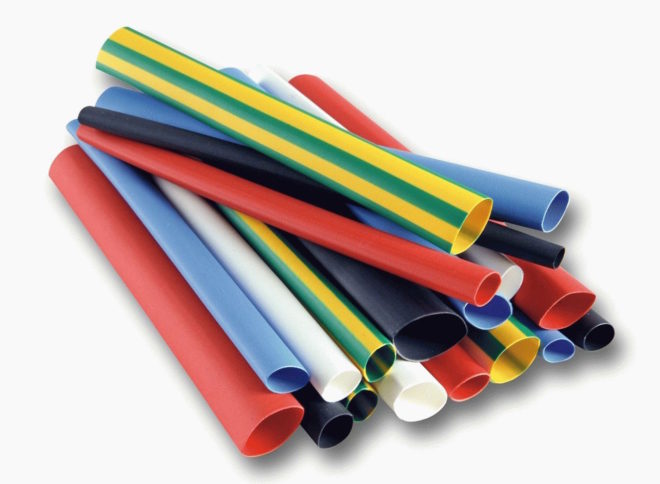

One of the parameters of heat-shrinkable products is their resistance to various operating environments. Based on this characteristic, the tubes are of the following types:
- heat resistant;
- light stabilized;
- oil resistant;
- petrol resistant;
- chemically resistant.
The tubes are round, oval and flattened in shape. It has practically nothing to do with installation, everything is purely for ease of transportation and storage. Oval and flattened products have thin walls and are transported and marketed in coils. Thick-walled and glue tubes are round in shape, they are supplied in a cut, they are not twisted into coils in order to avoid kinks.
An important parameter is the shrinkage ratio, this value indicates how many times the heat shrinkage for wires can be reduced in size. The larger this figure, the better, varies from 1: 2 to 1: 6. But accordingly, products with a high shrinkage coefficient are more expensive.
The main parameter of heat-shrinkable elements is the diameter before and after shrinkage. It is recommended to choose tubes with a diameter value after shrinkage slightly less than the diameter of the crimped wire.
The characteristics of heat shrinkage are described in this video:
Required tool
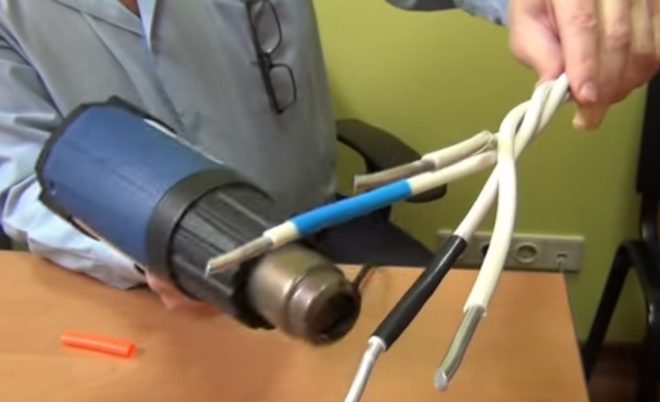

In order for the heat shrinkage to work as intended, it must first of all be heated. This means that any sources of heating will be needed.It can be:
- industrial dryer;
- heat gun;
- a propane-butane gas burner (the main thing is to set it up so that the flame is soft and yellow);
- ordinary household hair dryer;
- lighter or matches.
The main thing is to create a stream of hot air or an open flame. In some emergency cases, when nothing is at hand, they even dip the tube into boiling water.

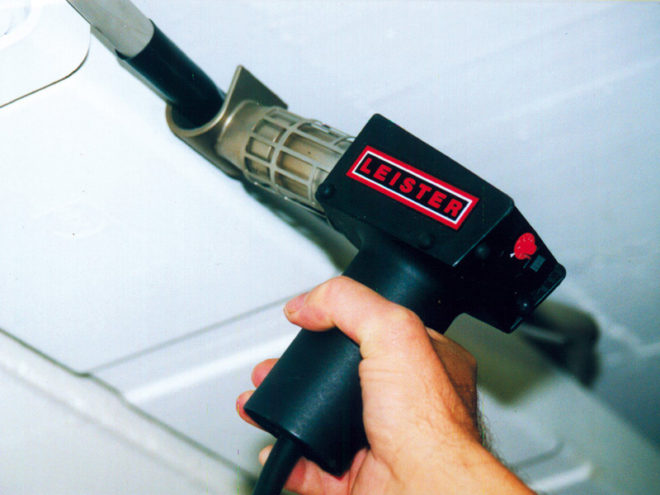
The best option would be an industrial hair dryer or heat gun, because these devices are safe and convenient to use, they can be used to adjust the temperature. The kit also includes additional attachments to facilitate the installation process in hard-to-reach places. But such a tool is not cheap, buying it only in order to insulate the wire connections in the junction box is not economically viable. It will be good if you can rent it or borrow it.
Shrinkage
It is quite simple to sit down the tube with your own hands at the place where the wires are connected, this is just the case when special skills and the invitation of a professional are not required.

The most important thing is not to forget to put it on one of the conductors before they are connected to a common electrical unit.
And then follow a certain sequence:
- Beforehand, the tube must be heated to half the required temperature. In the case of thin-walled products, this point can be neglected, but for a tube with thick walls and a large diameter, it must be performed.
- Pull the tube over the connection and start heating. Try not to exceed the temperature specified by the manufacturer. If you use a heat gun, this is easy to do by setting it to the desired degrees. Please note that if the required temperature is exceeded, the material may overheat, and the tube may melt or twist, or the shrinkage will turn out to be wavy. Heat from the middle of the piece to be fitted.
- When the central part is firmly settled on the joint surface, begin to move the heating source alternately in both directions. Move the flame or air stream constantly and evenly from the middle to the edges to avoid overheating in one place.
- The correct shrinkage is smooth, there should be no bulges or bumps on it. If you are using a glue tube, note that glue should come out at the edges after the shrinkage has finished. Let the assembled heat shrink cool completely.
How to use heat shrink, see the following videos:
Useful Tips
- If you are using a thick-walled tube, then first degrease the surface that it will crimp. To do this, soak a cloth in a grease-free solvent and wipe.
- It is very important to choose the optimum temperature for shrinkage. A good manufacturer will always indicate this figure on the tube itself or on the general packaging (ask the seller). If there is no such data, focus on a temperature of 120 to 150 degrees.
- Before placing the tube on metal surfaces, they must be deburred with sandpaper.
- If you are going to seat the tube on steel or copper conductors of large cross-section, preheat them. These materials have high thermal conductivity, due to which, at the time of shrinkage, heat can be removed from the heating site, which will affect the quality.
- When you cut the tube, do it carefully so that the edges are smooth and free from burrs. Otherwise, during shrinkage, the tube may burst, shrink unevenly or go in waves.
As you can see, polymer tubing as an insulating material is very effective, reliable and safe. In principle, everyone can afford to use them. The price range is very wide and depends on the manufacturer, size, color, glue availability and additional parameters.Accordingly, the price will be the quality - either these are inexpensive Chinese pipes, or 160 euros per 1 m from a German manufacturer with a worldwide reputation.




