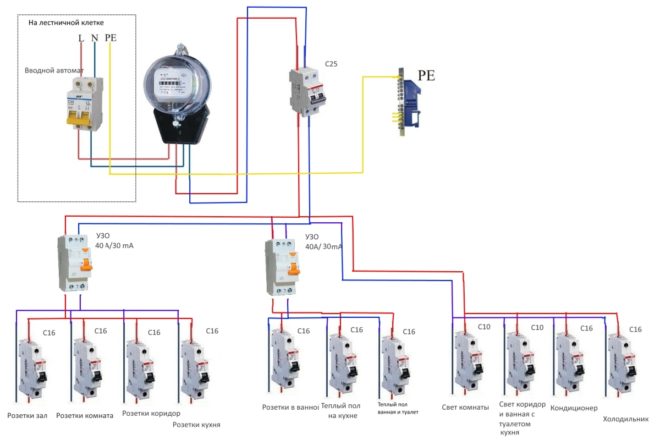
RCD in electrics - what is it?

To date, many people, even not professionally connected with electricity, have heard of such a concept as an RCD. What it is? Where are these devices used? What is their functional purpose? Can a modern electrician do without an RCD? You see how many questions there are. Let's try to give answers to everything.
To understand thoroughly, you will need at least a technical education, because the principle of operation, connection diagram, design features of this device are quite complex. We will not go into such a jungle, and we will briefly tell you the main points so that you can at least correctly imagine what an RCD is. In electrics, such protection elements are used relatively recently. Twenty years ago, not a single dwelling was equipped with such devices, and now it is already difficult to imagine a switchboard without them.
In order to understand exactly how this device works, it is advisable to first figure out what an RCD is for?
Content
The main purpose of the device
Do you know how RCD stands for? Residual current device. Most mistakenly believe that circuit breakers (in the common people called automatic machines) and RCDs are one and the same.

Here it is important to grasp what is the difference, what and what protects each of these devices?
The circuit breakers protect the supply voltage. For example, every room in your house is powered by a separate machine. In the event that a short circuit or overload occurs in some electrical branch, the circuit breaker will turn off and thereby cut off the damaged section, saving the general network.
An RCD is installed in an apartment to protect people. The decryption itself says about this - "protective shutdown", that is, the element protects a person from accidental electric shock.
How does he do it?
Our homes are now crammed with a huge amount of household appliances, some of which are very powerful. At the same time, the electrical wiring has a certain service life and over time there is a possibility of insulation failure, which will entail connecting the wiring to the ground. As a result, the current will not begin to move along the specified path, but a leak to the ground will occur, a person can become a conductor for this. Let's also consider this with an example.
Suppose that an insulation breakdown has occurred in some electrical household appliance (kettle, dishwasher or washing machine, vacuum cleaner).

As a result, the body of the electrical appliance will have a certain potential. If you touch the case, you can get an electric shock. As you can see, in order to earn an electrical injury, it is not necessary to climb into an outlet, everything is much more commonplace, therefore it is so important to protect yourself from such accidental touches.
Of course, if there is a ground loop in the room and switching devices (sockets) with grounding are installed, they will save you from electric shock. But sometimes the electrician in our apartments does not fully comply with the standards and rules. You must admit that not everyone and not every room has sockets with a grounding contact, and we have no confidence at all about the quality and reliability of the ground loop.
Clearly about the RCD in the video:
This means that you have to protect yourself by installing an RCD in the distribution boards. As soon as a leakage current appears, it turns off, thus saving a human life.
An equally important purpose of the device is considered to be the protection of houses from the possibility of ignition and fire, which occur when the insulation of the wiring is broken.
Performance characteristics
If you have never met an RCD and are trying to mentally picture yourself a picture of what it is, it is enough to remember an ordinary machine.
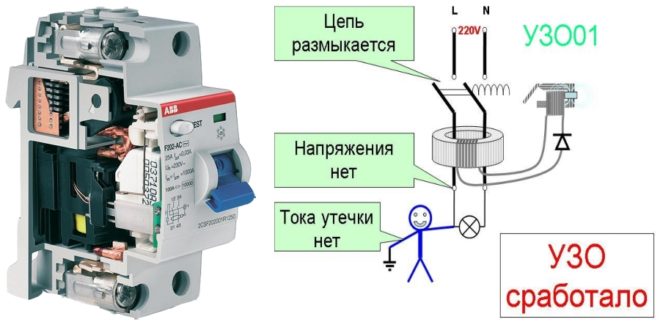
Similarly, with this switching device, modern protective automatics of the power grid cannot do without an RCD. Serves as a device for switching circuits (that is, it monitors the current flowing through the circuit and, if it detects a leak, breaks it).
If you look at the case, you will find on it a lot of letters and numbers that characterize the device. How are they decrypted?
- At the very top, the plant or manufacturer of the device is indicated.
- The model name follows.
There is not always an abbreviation here - RCD, sometimes they write VDT (differential current switch), or UDT (differential current device). You can consider all this as synonyms - in principle, it is all one and the same device.
- Then the digital value of the operating current is written (this is the maximum value of the current that this device can switch).
- The following are the standard parameters of the household electrical network - voltage 220-230 V, frequency - 50 Hz.
- Next comes the leakage current (this is the value at which the RCD will trip).
- Then the type of device is indicated (it can be written in letters or drawn with icons, which we will talk about below).
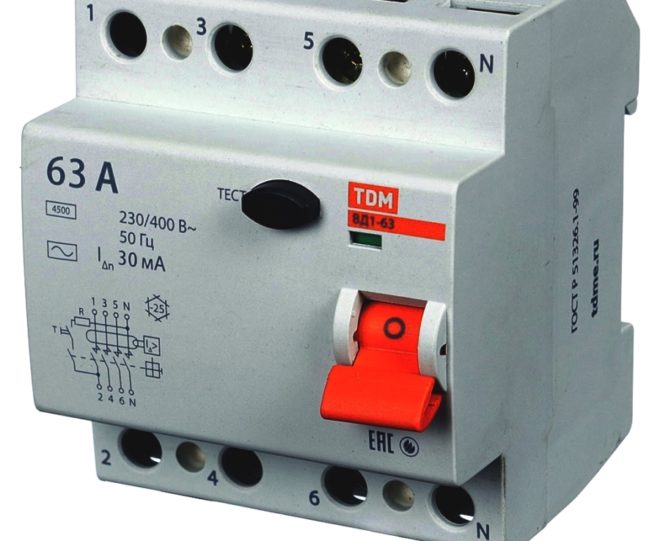

- Operating temperature range. As a rule, for an RCD, the minimum limit is -25 degrees, the maximum is + 40.
- The following current value corresponds to the conditional rated short-circuit current. This figure means what maximum short-circuit current the RCD withstands without tripping, if at the same time it is protected by a suitable machine.
- Single-line RCD diagram.
Different manufacturers can change the data on the case (someone adds additional characteristics, other companies, on the contrary, remove some parameters). But the basic information is always indicated, especially such important information as the magnitude of the currents (leakage and operating).
How to choose the right RCD - in the following video:
As you can see, the device has a lot of characteristics, depending on them, various types of RCDs are produced. How and how they differ from each other, we will talk below.
Varieties
All devices are classified according to several parameters:
- by the form of current leakage;
- by mode of action;
- by time delay;
- by design.
Let us briefly consider what the features are and why this or that RCD is needed.
By the shape of the current leak
All devices, depending on the leakage current, are classified into three types:
- "AC". The most common and affordable RCD. It works to shutdown if an alternating sinusoidal current leakage occurs in the circuits (smoothly increasing or instantaneous). The body of such an RCD has the letter designation "AC" or the icon:
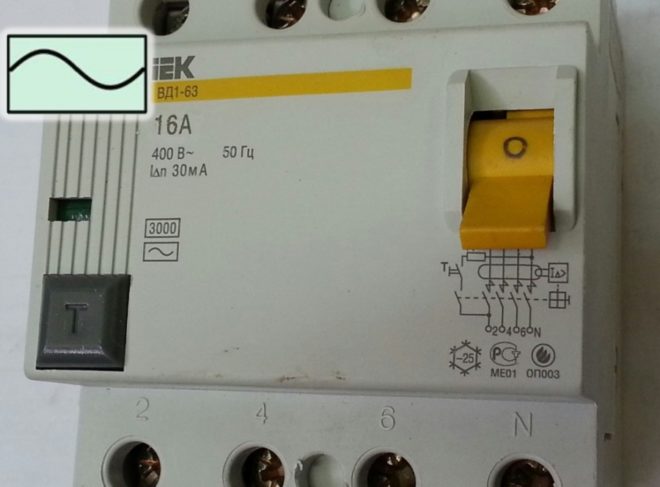

- "AND". It turns off if leakage currents of alternating sinusoidal or constant pulsating form instantly appear in the circuits or smoothly increase. Such RCDs are used everywhere. True, due to the fact that they control not only the alternating current, but also the direct current arising in the power supply, their price is much higher.
In the passport documents for some household appliances, specific recommendations are sometimes given that it must be connected through an RCD of type "A".
On such RCDs you will find the letter "A" or an icon that looks like this:
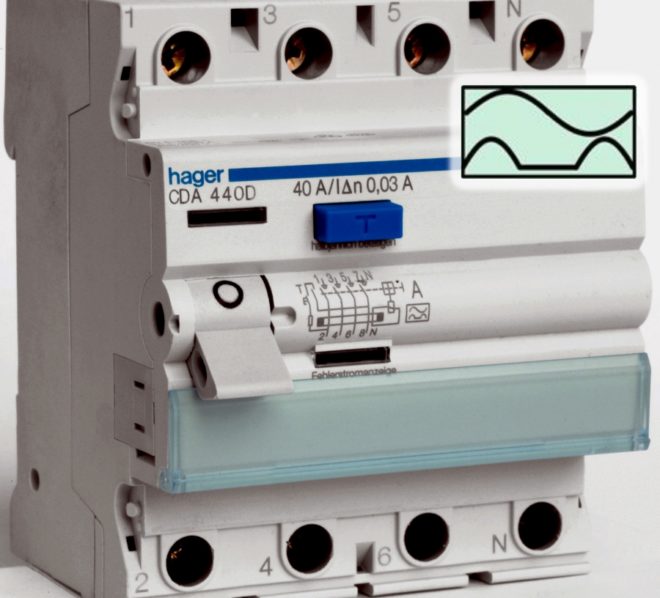

- "IN". This RCD operates with three types of leakage current: pulsating constant, rectified and sinusoidal variable. Such devices are most often used for industrial facilities; it is not worth purchasing them for a garage, house or suburban building.
You will define the designation of such devices in the same way - by the letter "B" or by the icon painted on the case:
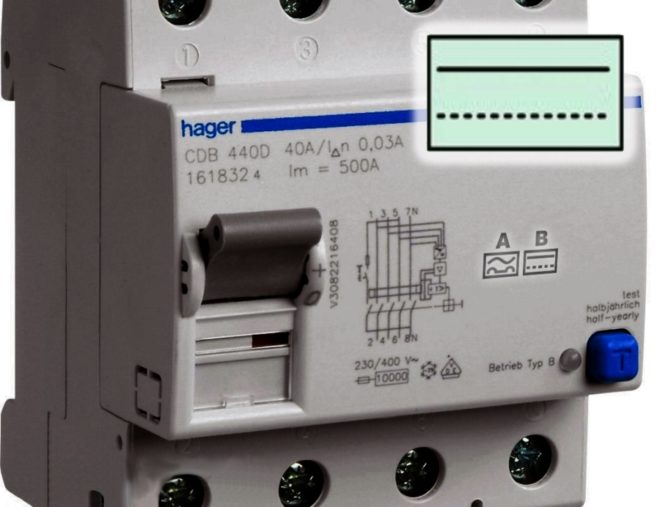

The tripping time for the above types of RCDs ("AC", "A", "B") varies from 0.02 to 0.03 s.
By the principle of action
According to the principle of operation, RCDs are divided into electronic and electromechanical.
With the latter, everything is much simpler, electromechanical devices do not depend on the supply network. For their operation, it is enough that a current leak occurs in the damaged electrical branch.
For electronic RCDs, current leakage is not enough, they still need a supply network. For such a device to disconnect the damaged area, there must be power from an external source for an electronic amplifier built into the electrical circuit. Due to this, electronic RCDs are considered not as reliable as electromechanical devices, respectively, they are not so widespread.
To make it clearer for you, consider this theory with an example. Suppose that the socket line from which the microwave oven is powered is protected by an electronic type RCD. By coincidence, two emergencies occurred simultaneously:
- the zero core is damaged in the access switchboard;
- inside the microwave oven there was a damage to the electrical wiring, as a result of which the phase was shorted to the case.
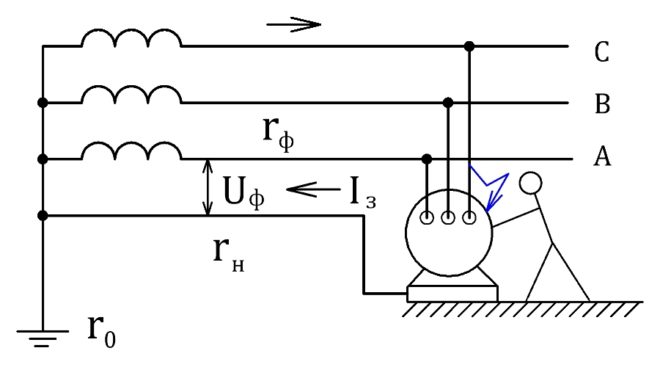
In this case, the microwave housing was at a dangerous potential. If you accidentally touch the oven, the electronic type RCD will not work, because its built-in circuit remained unpowered due to zero damage in the shield. The likelihood of such a case is minimal, but it can happen.
A way out of such situations was invented by foreign manufacturers of electronic devices. They decided to supplement the RCD housings with electromagnetic relays that will disconnect the protected circuit as soon as the power from an external source is lost.
We advise you to still install an electromechanical type RCD, although it is more expensive than an electronic one.
By time exposure
According to this characteristic, all devices are divided into two types: "S" and "G".
RCD type "S" has selectivity, that is, it works after a certain time (from 0.15 to 0.5 s). Devices of this type are usually used when several of them are installed in a chain.
Let's consider a small example. Let's say there are two outlet groups in a home switchboard. Each of them is protected by an RCD having no time delay (type "A" or "AC"), and the input itself is equipped with a type "S" protective device.
If a current leak occurred on one of the outlet groups and the RCD protecting these sockets did not react for some reason (electricians call a similar situation skipping protections), then after a certain time the device at the input will turn off.
Note! The selectivity of the action of the RCD is not always achieved by a time delay, sometimes this is achieved due to the settings for the differential current (this method is now more common).
The device of type "G" has the same selectivity, its difference is in smaller limits of the time delay (from 0.06 to 0.08 s).
About the main characteristics of the RCD in the video:
By design
Structurally, RCDs differ depending on the number of poles:
- in single-phase voltage networks, two-pole models are used;
- in three-phase voltage networks, an RCD with four poles is mounted.
By other parameters
There are several more parameters by which RCDs are classified:
- By installation (stationary and portable).
- For installation (using fixed wiring or using flexible wires with extension cords).
- Equipped with protections. There are devices without protection at all, and there are devices with built-in ones - against overload and short-circuit current.

- If possible, regulation of the differential current (unregulated, adjustable smoothly or discretely).
We have provided you with information on what an RCD is in electrics. We hope that it is clear from the article that a modern automation and protection system cannot do without this element.If your property is dear to you, and even more so human life, then do not neglect the installation of residual current devices.