Types of wires and cables for laying household wiring
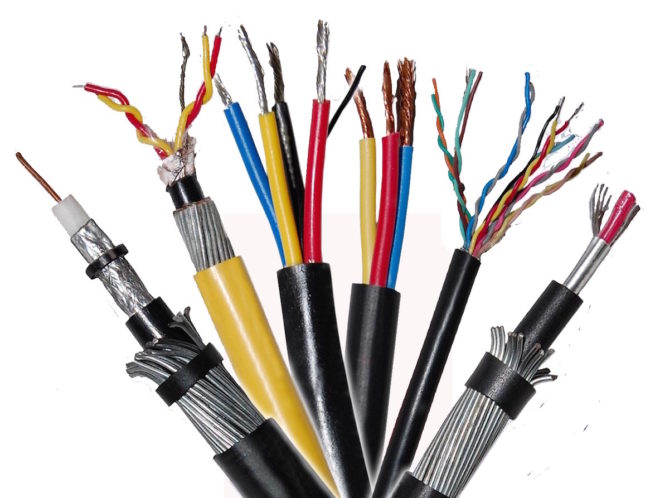

An electrical wire, cable or cord is a copper or aluminum conductor through which current and insulation pass, which protects the line from a short circuit, and a person from being exposed to dangerous voltage. All types of wires differ only in the thickness of the metal cores and the insulation material, which determines its resistance to heat, environmental influences and the likelihood of ignition.
Content
The main types of wires
First of all, the division is made according to the purpose. The very first types of electrical wires and cables were power cables, designed to deliver electricity to the consumer. Then it turned out that it is more profitable to use alternating current to transmit electricity and the higher the voltage, the less losses, so the search for its optimal values began. As a result, power wires are divided between those that transmit electricity from power plants to cities (with a voltage of 20-150 thousand volts) and those that directly bring it to consumers' homes (110-380 volts).

With the invention and development of telephone communication, corresponding wires appeared - since telephones do not need a lot of voltage to work, it is too expensive to use power wiring for their lines. In addition, to connect a large number of subscribers, cables with an appropriate number of cores and protection against moisture were needed.
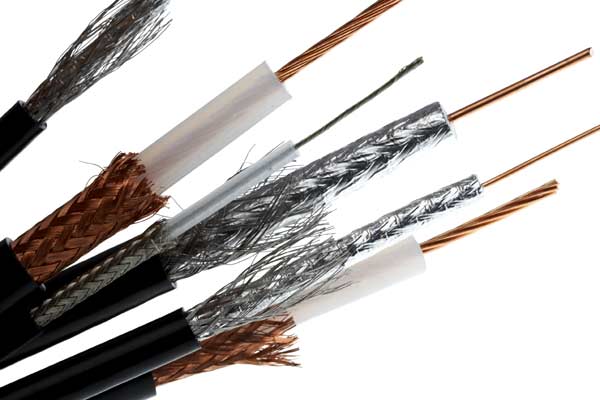

With the development of radio and television, special wires were needed to connect the signal reproducing device to the antenna. One of the main requirements for them is the presence of shielding, since without it, a weak transmitter signal will be distorted by parasitic currents.
When it became necessary to connect computers into a single network, new types of cables and wires were needed - specifically for these purposes. Initially, telephone lines were used for these purposes, but the data transfer rate remained at a very low level. A breakthrough in this area came with the invention of optical fiber, which was used to transmit signals over long distances. Twisted pair cables were used to connect local local networks.
In addition to the main types of wires, non-standard ones are used - for example, for heating, lighting, or simply decorative.
Power wires
Designed for the transmission of electricity from power plants to distribution transformers and further to the end consumer. In the first case, wires are used that are designed for operation in the open air and withstand voltages up to 150 kV - the optimal value for transmitting electricity over long distances.
Household power wiring is designed for alternating current with a frequency of 50-60 Hertz and voltage up to 1000 Volts. A classification is often used according to the material of current-carrying conductors, which can be made of aluminum, its alloys or copper. Aluminum is cheaper to manufacture, while copper has less resistance to electric current, so they have a smaller section. It is preferable to use copper wiring - it is more durable and more reliable, but due to the price, aluminum is still used quite often, and in power lines and in general - almost everywhere.
VVG is the market leader
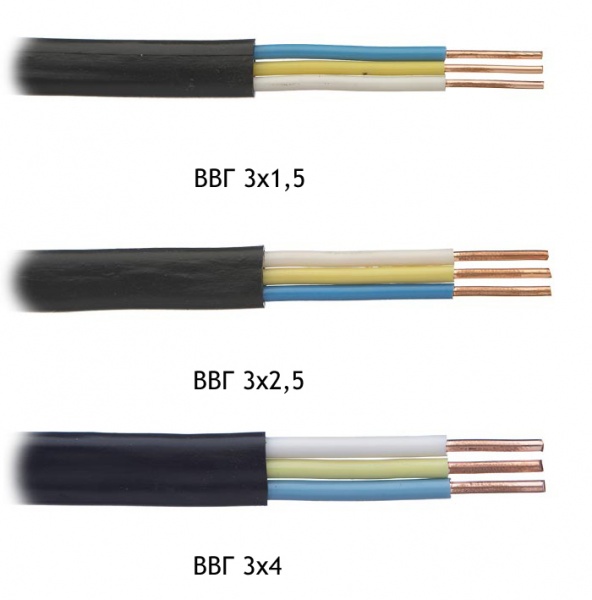

Double PVC insulation cable for power grids - multi-colored on each core and common cambric. Current-carrying conductors, single or multi-wire, with a cross section of 1.5-240 mm².Has the following varieties:
- AVVG. The letter "A" before the name says that the conductors of the cable are made of aluminum.
- VVGng. Wire insulation is non-flammable over a wide temperature range.
- VVGp. It differs only in externally - flat shape.
- VVGz. High-security cable - inside it all empty spaces are filled with a rubber compound.
NYM cable
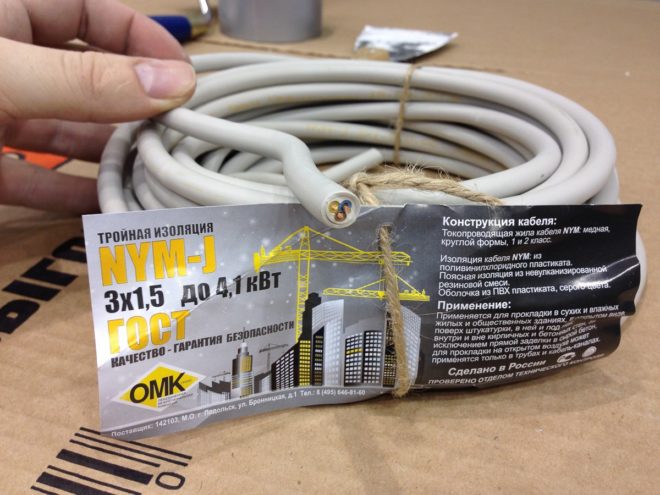

It is made according to European standards and although it is similar in conductive properties to VVG wires, it surpasses domestic counterparts in insulation class, since during manufacture, the voids between the veins are filled with coated rubber. It is manufactured with the number of current-carrying conductors from 2 to 5, with a cross section of 1.5-16 mm². Outdoor installation is permitted, but with additional protection from sunlight, as the insulation is not UV resistant. Unlike domestic counterparts, it can be laid with a bend radius of 4 of its diameters.
KG - flexible cable
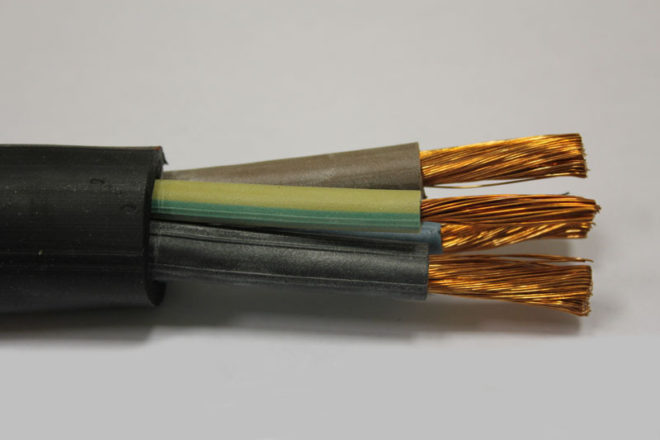

Without losing its properties, the cable can be operated at temperatures from -60 to +50 C °. It is most often used to connect electrical appliances to the network, and its cores are designed for a current frequency of up to 400 Hz, which makes it a good choice for use in welding machines. Current-carrying conductors are only copper multi-wire with rubber insulation. The number can be from 1 to 6, hidden under a common outer shell.
VBBShv - armored
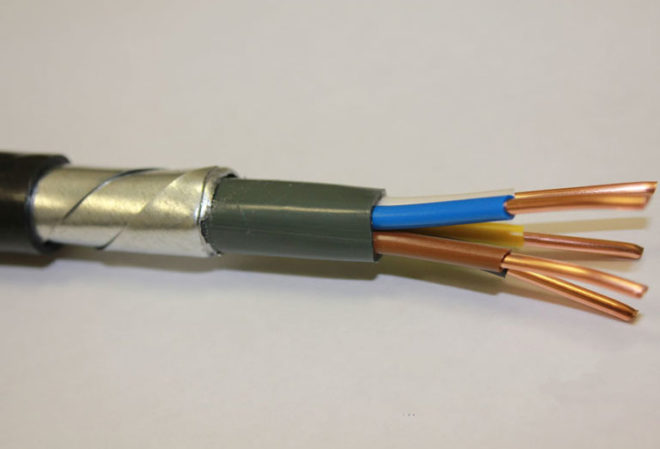
Increased protection against mechanical damage is provided by tapes with which the wires are wrapped before applying the main layer of insulation. Live conductors made of copper, separately insulated PVC, quantity - 1-5 pieces, consisting of one or more wires. Single cores are used for direct current transmission.
There is one limitation for using the cable - installation without UV protection is not recommended. The following types are used:
- AVBBShv - with aluminum conductors;
- VBBShvng - with excessive heating, the insulation does not burn, but smolders;
- VBBShvng-LS - minimum of smoke and gases during smoldering.
Telephone Cables
There are two types of wires and electrical cables - to connect the switchboard to the line and to connect individual subscribers to it.
- TPPep - cable with conductors 0.4-0.5 mm², shielded with alumopolymer tape. Some of its variants allow connecting switchboards for 500 subscribers to the station. For the convenience of the telephonists, individual wires are twisted together in pairs, and are additionally collected in groups of 10-20 pairs, although such a division may not be available. Shielding and protective layers of the cable allow it to be used in all existing cable ducts - underground and overhead.

- TRV is a flat wire with two or four cores and PVC insulation, with which one or two subscribers are connected to a switch cabinet. Designed for installation of telephone wiring inside buildings. It can be operated at air humidity up to 80%.

- TRP - analogue of TRV, but with PET insulation. This is a more stable material, so the TRP can be installed outdoors.
- SHTLP is a flat cord with a cross-section of stranded conductors from 0.08 to 0.12 mm². Its purpose is the installation of telephone lines and connections inside telephone sets (during manufacture or repair).

- PRPPM is a flat wire with two conductive cores with a cross-section of 0.9-1.2 mm² with reinforced double polyethylene insulation. It can be laid in the ground and on supports, retains its properties at -60 to +60 C °.

Antenna cables
Their main task is to transmit the signal from the antenna to the receiving device without distortion. Structurally, it is a single copper core through which the signal is transmitted. To protect against mechanical damage and eliminate frequency overlays, the core is insulated with a layer of polyethylene foam with a thickness of 1-2 mm. The main core is protected from parasitic currents by a shielding layer made of foil or braid. Outside, everything is sewn up with a PVC sheath.

Despite their simplicity, these cables have many characteristics to choose from:
- Electrical resistance of the main conductor - affects the maximum possible wire length.
- What signal frequency the wire is designed for. For DV and VHF communications, the required parameters will be very different - the higher the frequency, the stronger the current spreading over the surface, therefore, in the second case, it is necessary to use a cable with a multi-wire core.
- Shielding quality - here it is advisable to take into account the nature of parasitic currents and select a screen made of solid foil or braid to neutralize them.
- It is imperative to consider where the cable will be laid - whether it needs protection from mechanical stress and resistance to temperature extremes.
For more information on choosing an antenna cable, see this video:
Computer cables
By analogy with telephones, two main types of wires are used here - for connecting end users with a switchgear and connecting the latter with the World Wide Web.
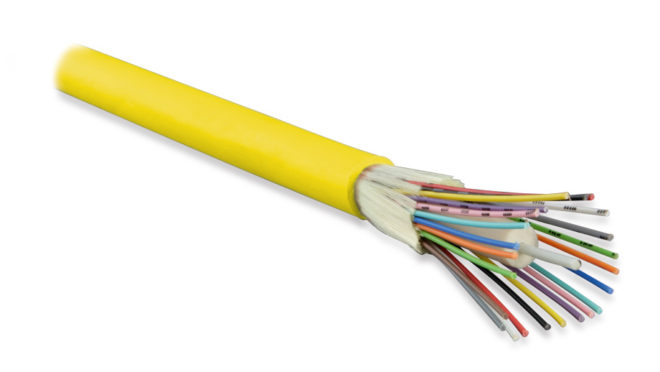
Optical fiber used to transmit data over long distances is not an electrical cable, since it is not an electric current that flows through it, but light pulses that still need to be converted into electrical ones. To connect such wires, you need special equipment and highly qualified personnel, so they are practically not used in everyday life.
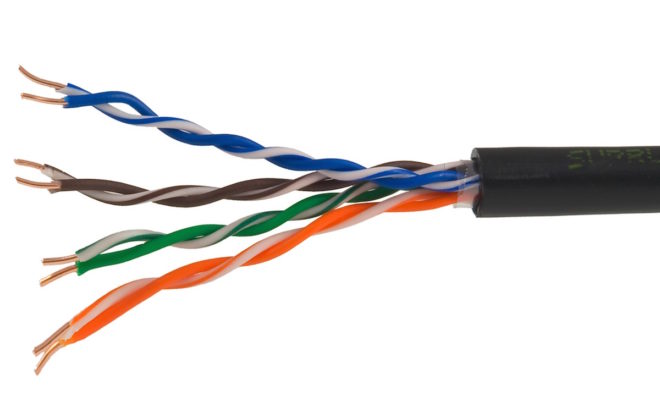
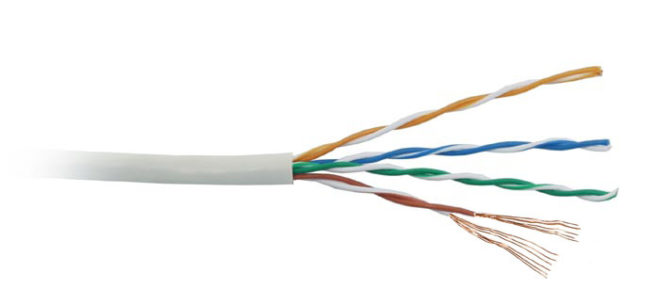
Twisted pair. A wire that is well known to Internet users - it is such a cable that comes to a computer and connects to its network card. Structurally, it consists of eight current-carrying conductors, twisted in pairs. Each core has a separate PVC or propylene insulation and, depending on the classification of the wire, all together they can be covered with additional protective and shielding layers:
- UTP - all wires are twisted in pairs, and from above are covered only with an outer sheath;
- FTP - there is a foil layer screen under the outer shell;
- STP is a double shielded cable. There is a separate shield on each twisted pair and is all surrounded by a braid of copper wire;
- S / FTP is also double shielding, only here a foil shield is used.
Special purpose wires
The same types of electrical wires are used if they need special properties that ordinary cables do not have and for connecting electrical equipment in those places where the use of standard conductors for some reason is difficult or even impossible. For example, ordinary wires cannot be used when connecting electric ovens that heat up to high temperatures. The same applies to baths or cellars, where, in addition to temperature, the humidity factor must be taken into account.
In addition to the effects of temperature and moisture, the likelihood of mechanical damage must be taken into account, especially for wires that are laid underground.
Non-standard power wires

RCGM. Flexible single-core wire for installation of power wiring in places with high temperatures - does not change its characteristics in the range from -60 to +180 C °. The insulation material can withstand voltages up to 660 Volts, is resistant to vibration, 100% air humidity, does not deteriorate from mold and contact with aggressive liquids - varnishes or solvents.
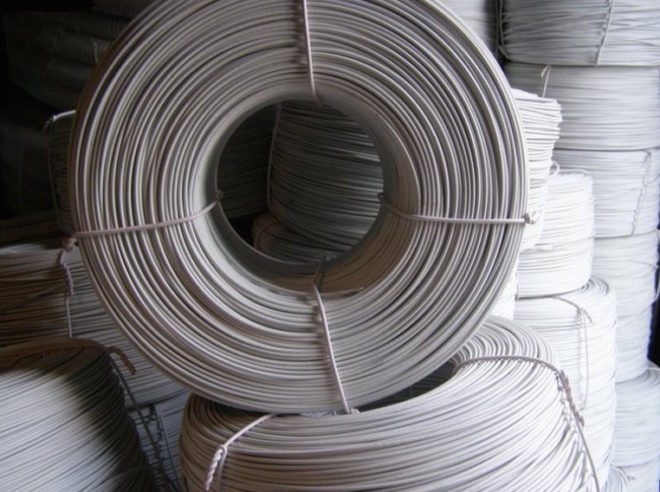

PNSV. Single-core steel wire in PVC insulation with a conductor cross-section from 1.2 to 3 mm². The material and cross-section are selected in such a way that the wire heats up when an electric current is passed through it. Most often, it is used as a heating element in warm floors or on construction sites when pouring concrete in the cold season - this allows the use of concrete solutions at sub-zero temperatures.

Runway. Stranded single-core wire, cross-section from 1.2 to 25 mm² with double insulation.Designed to work in artesian wells, where it is used to connect power to the motors of electric pumps - i.e. not afraid of water and high pressure.
Custom decorative wiring
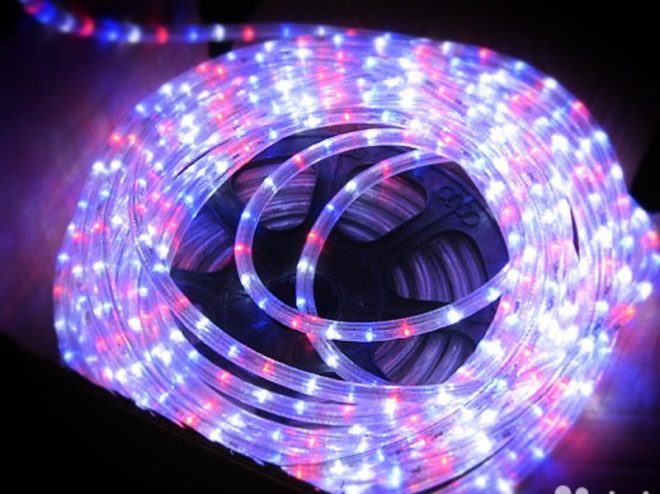

LED cable. In addition to the main conductors, it has an additional circuit to which LEDs are connected. They are located under the transparent outer sheath at a distance of about 2 cm from each other and begin to glow when the wire is connected to the network. The connection diagram of the LEDs is serial-parallel, which allows you to cut the wire anywhere, and also, in case of damage, shows the location of the cable break. If you choose wires with different colors of LEDs, you can create whole pictures, which determines the most popular niche for using such a cable - stage effects and the connection of the equipment necessary for them.
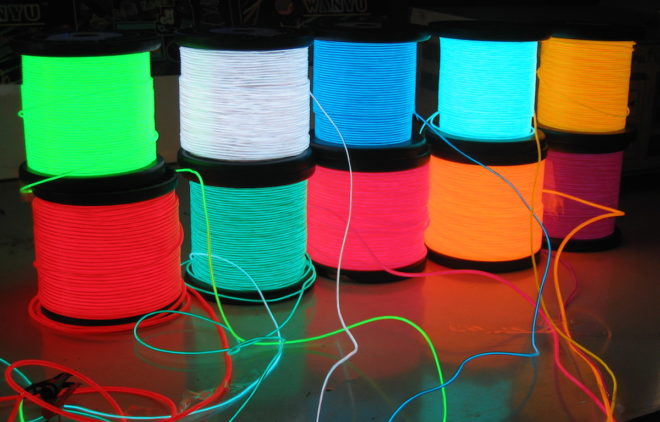

Electroluminescent wires - work due to the phenomenon of pre-breakdown electroluminescence of solids. The main core of the wire is covered with a phosphor and a dielectric layer. From above it is wrapped with two thin wires and a dielectric is applied to everything - transparent or colored. In fact, the main core and additional wires are a capacitor, which requires alternating current with a frequency of 500 to 5.5 thousand Hertz and a voltage of about 100-150 Volts. When charging and discharging a capacitor, under the influence of an electric field, the phosphor begins to glow along its entire length. In all respects, such a wire is better than neon tubes - it has less energy consumption, it is cheaper to manufacture, is not limited in length and can freely change its shape.

Decorative wiring also includes the one that is used for the "retro" style. These are ordinary power cables, but it is assumed that they will not be hidden in the wall, but laid along its surface, with appropriate requirements for reliability and appearance of the insulation. Most often these are two or three-core wires with conductors twisted together.
These are the main cables for the transmission of electric current, radio signals and digital data. Of course, there are still quite a lot of varieties and analogs, only the listing of which will take a lot of time, therefore, for example, those of them were chosen whose characteristics most fully correspond to the class of wires they represent.