How to choose the right RCD for a water heater and other equipment in the bathroom?

Modern electrical safety requirements for a household network, whether in an apartment or a private house, provide for the installation and connection of two main types of protection. The first is the circuit breakers, which protect the network from short circuits and overloads. The second element is a residual current device (RCD), which ensures the safety of human life from electric shock at the moment of touching live parts or the occurrence of leakage currents. Such protection is especially important in rooms with high humidity, that is, in the bathroom. Therefore, we will dwell in more detail on the question of how to choose an RCD for a water heater or washing machine.
Content
How does an RCD work and what is its need?
First, you need to understand the difference between RCDs and circuit breakers.
The circuit breaker is the main protection of the supply network. In the event of overcurrents at the time of overload or short circuit, the switching device will react to the overcurrent and turn off, cutting off the emergency section and saving the entire network from damage.

The main function of the RCD is not to protect the network, but the person, and this device reacts to small values of leakage currents. How does this happen?
In our homes now there is a huge amount of various household appliances, and some of them have a fairly high power. The service life of electrical wiring is not eternal, the longer it is in operation, the greater the likelihood of insulation failure. Damage to the insulating layer entails the connection of the wiring to the ground, as a result, the path of the current flow changes, now it flows to the ground. And in some cases, a person can become a conductor for current leakage.
More clearly about the principle of operation of the device on video:
Modern washing machines and water heaters are considered to be appliances with a higher energy efficiency class. They take the maximum power during the period when the heating element is working and the water is heated (about 3-3.5 kW). For electrical wiring, this is a very heavy load that can cause premature aging of the insulation.
Suppose a breakdown of the insulating layer occurs in the washing machine, as a result of which the case is energized. By touching a typewriter, a person can get under the influence of electricity.
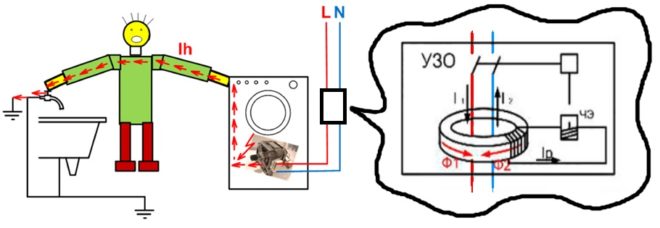
To protect yourself from a similar situation, you need to put an RCD for the washing machine.
If an earth leakage current occurs, the device will shut down and stop supplying voltage.
With the consumer, the RCD is connected in a single circuit in series, and its principle of operation is based on measuring the difference between the input and output current values. Ideally, it should be equal to zero, that is, what value of the current went in, it came out. As soon as a leak occurs, the output will have a different reading, exactly less by the amount of current that has left along the other path. The measured difference will change accordingly. As soon as the leakage current reaches the value for which the device is designed, it immediately responds and shuts down.
There are no special difficulties in connecting the device. In the circuit, first there is an automatic switch, after it an RCD, from the output contacts of which the wires go to the consumer, that is, the power outlet to the washing machine or boiler.
Features of the use of difavtomats
In order not to mount separately the RCD and the machine for the washing machine or for the boiler, you can replace these two switching devices with one device. This is a very popular differential automatic machine that has been widely used in the electrical household network.

The device is combined in one housing and combines the protective effect of both an RCD and an automatic device.
The difavtomat has one drawback, it is a high price. That is why many prefer him two switching devices in series (RCD and a conventional circuit breaker).
But one has only to imagine how many machines and RCDs will be needed for the bathroom, if some have a washing machine, a water heater, and an electric boiler there. And in private houses, the room is often adjacent to the sauna, where there is a stove. What kind of switchboard should be in order to accommodate so much automation. It may happen that there is not enough space on the din rail for all devices. Therefore, it is recommended to put a separate difavtomat on the washing machine, boiler and other household appliances in the bathroom.
Pros and cons of RCDs or difavtomats in the following video:
Parameters and characteristics of difavtomats
To determine which RCD to install for a washing machine or water heater, first familiarize yourself with the main parameters and characteristics of the device:
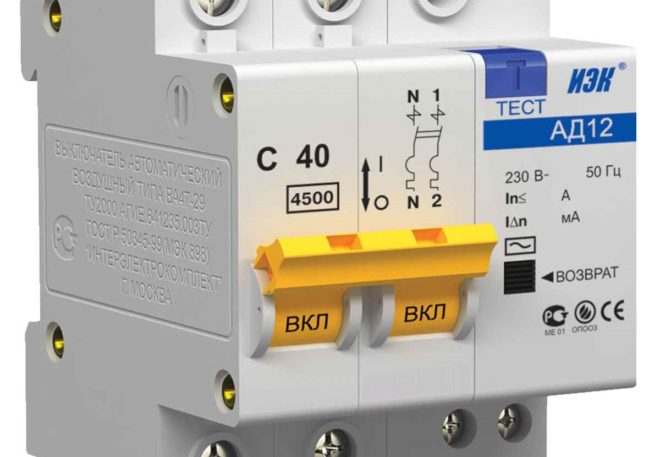
- Depending on which network the difavtomat will be installed in (single-phase or three-phase), a two-pole device (for an operating voltage of 220 V) or a four-pole device (380 V) is selected. Please note that the rated operating voltage must be indicated on the device case.

- Rated current. This is the amount of current, measured in amperes, that can flow through a switching device during a long period of operation. The standard range of rated currents is as follows: 6, 10, 16, 20, 32, 40, 50, 63 A.
- Time-current characteristic ("B", "C" or "D"), this parameter expresses the dependence of the operation time of the machine on the current flowing through it.
- Rated differential current. This is the amount of current leakage to which the difavtomat will react and turn off. There is also a standard range of differential currents - 10, 30, 100, 300, 500 mA.
- Rated breaking capacity. This parameter represents the maximum value of the short-circuit current that the differential automatic device is able to disconnect and then remain in working condition.
- Temperature Range. It usually ranges from - 20 degrees to + 45.
All these parameters are indicated on the device body.

There you will find a wiring diagram, the value of the rated frequency of the mains (50 Hz), the type of built-in RCD (electronic or electromechanical).
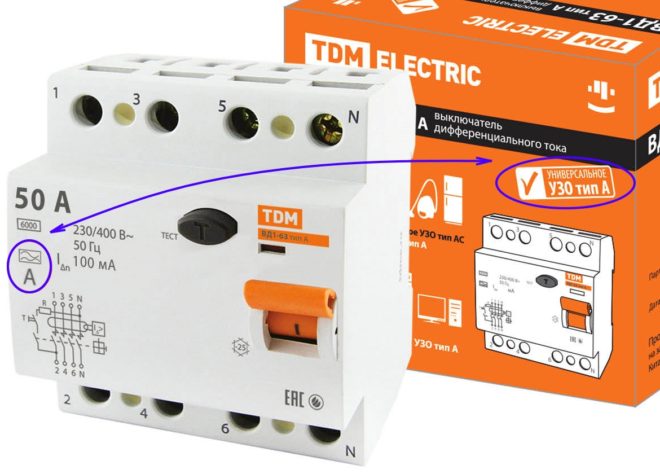
Also, differential automata are of three types, depending on the form of current leakage to which they react:
- "A" - for alternating sinusoidal and constant pulsating current forms.
- "AC" - for variable sinusoidal current leakage.
- "B" - for variable sinusoidal, constant pulsating and rectified forms of current leakage.
Choice of protection device
Based on the above characteristics, an RCD is selected, but do not forget to take into account the conditions of the bathroom (high humidity).
Give preference to type "A" devices that react to AC and DC current. Despite the fact that a sinusoidal alternating current flows in our power grid, modern household appliances are equipped with special power supplies based on electronic semiconductor elements. Due to this, the AC sinusoid in the power supply is converted into a pulsed half-cycle. And if the leak is of this nature, then a cheaper device of the "AC" type will not react to it and will not work.
Carefully consider the passports for the washing machine and water heater when you are going to buy an RCD.
It is for equipment installed in the bathroom that manufacturers indicate the type of device needed, most often it is "A".

Some differential machines have an additional block in design, with the help of which consumers are disconnected when the neutral wire is broken in the network.
For household appliances in bathrooms, it is recommended to install an RCD with a rated residual current of 10 mA. In terms of the time-current characteristic, type "C" is preferable.
If you are not sure that you can choose a protective device yourself, then go shopping in retailers that have a good reputation. Qualified sales consultants will provide you with the necessary assistance, tell you which manufacturer to give preference to, select the right device according to your financial capabilities.
Malfunctions
It is not uncommon for an RCD to turn off when a water heater or washing machine is turned on. There are a number of reasons for this:
- the water heater itself or the machine is faulty;
- installed RCDs or difavtomat do not correspond to the parameters of the electrical network;
- there is a short circuit in the power cord;

- damaged engine, power supply unit or heating element;
- the installation of an RCD for a washing machine or water heater was made with errors;
- voltage surges or current leaks have occurred in the power grid.
An example of finding and eliminating one of the faults in which the RCD of a water heater knocks out, in the video:
If you choose and install the RCD on the boiler and the washing machine correctly, you will ensure the performance of the equipment for a long time during washing and heating the water, protect it from current leaks and fires. And most importantly, protect people from being hit by electricity. Therefore, think about protection in advance, so that later you do not have to eliminate the consequences.




