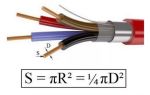
Technical characteristics of the PVS cable
When choosing a PVA cable, technical characteristics are not always put to the fore, since its main advantage is cost. However, this does not prevent the wire from being sufficiently reliable, with the correct selection of the cross-section and use in the recommended conditions.
Content
Operational and technical characteristics
The recommended scope of use of PVA cables is various connections of electrical equipment: movable and fixed. A distinctive feature is its excellent flexibility, which allows its use in conditions of multiple bends.
The purpose of the PVS cable is determined by the decoding of its abbreviation:
- P - wire (although it can also be called a cable);
- B - the cores of the wires are covered with polyvinyl chloride, like the outer sheath;
- C - connecting - this letter shows where it is recommended to use the wire.
The purpose of this cable excludes its use when installing internal wiring, although such a prohibition is not directly stated in GOSTs or the requirements of the PUE.
What the marking says
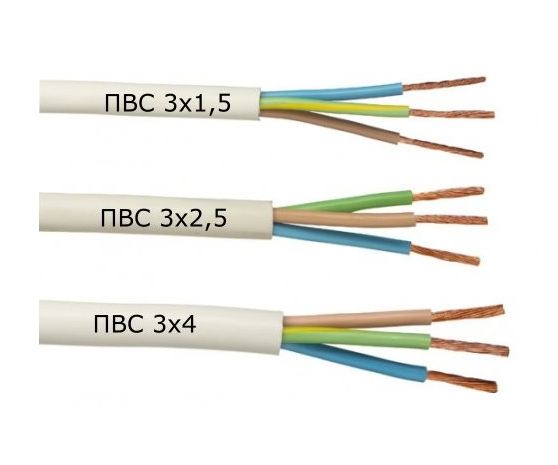

PVA cable is produced in several varieties, differing from each other in the number of current-carrying conductors and their cross-section, which is reflected in the cable marking. The following colors are used in the manufacture of insulation:
- The outer shell is most often white, but there are no obstacles to its manufacture in other colors - black, red, gray, blue, etc.
- The grounding conductor is connected to a green-yellow wire.
- To connect the neutral wire, blue is used.
- All other colors are used to connect the phase - one or more.
On the outer sheath, the manufacturer applies the following markings: PVA X * Y, where X shows the number of cores in the cable, and Y - the size of their cross-section in mm².
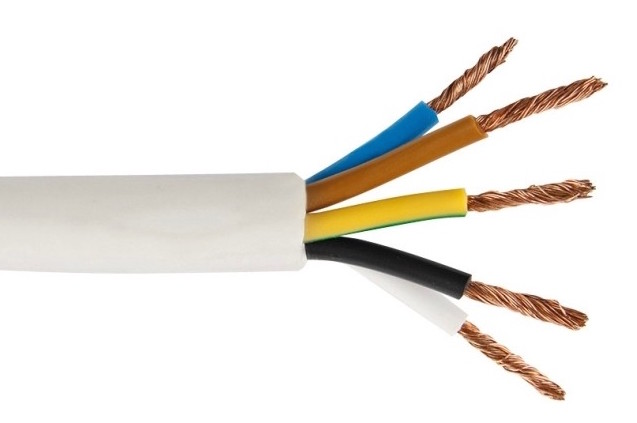
According to the number of wires and their cross-section, PVA cables are of the following types:
- Two-core - PVS 2 * (0.5-6)
- Three-core - PVS 3 * (0.75-10)
- Four-core - PVS 4 * (0.75-10)
- Five-core - PVS 5 * (0.75-10)
- Seven-veined - PVS 7 * (1-2.5)
The rest of the physical characteristics are shown in the table in the figure:
Technical characteristics of PVS
If you rely only on the main technical characteristics of the PVA wire, you might get the impression of its versatility, but still it is intended specifically for connections. The reason for this is the low shelf life of 6 to 10 years. In addition, the other technical characteristics of the PVA cable are not particularly distinguished by anything, therefore, despite the recommendations of the PUE, it is often used for installing hidden wiring.
- Working voltage - 660 Volts.
- Manufacturer's warranty - 2 years from the date of the start of operation.
- The temperature of use at which the wire insulation retains its properties is from -25 to + 40C °. There is a frost-resistant version of the cable, marked "Y", which can function at -40C °. Insulation must withstand long-term heating up to + 70C ° and short-term up to +80. Since the cable can be used on moving machinery, this also applies to the permitted installation temperature.
- The number of cores is 2-7.
- The humidity level at which the wire can be used is 98%.
- Service life - 5000 hours when installed as electrical wiring and 12000 hours when used to connect electrical equipment.
- Resistance to deformation, with bends in both directions with a radius of 6 cm - 30,000 cycles.
- The length of the wire coil for sale is 30 and 200 meters.
- Dielectric tests are carried out with an alternating voltage of 2000 Volts - the cable must withstand it for 5 minutes.
As you can see, all the technical characteristics of the PVA wire are designed for sufficiently large loads, electrical and mechanical.This is more than enough for domestic use, but choosing a suitable wire you still need to make careful calculations of the cross-section of the conductors.
What is the PVA wire used for, see this video:
additional characteristics
In addition to the standard version of the PVS cable, it has varieties for use in conditions of increased fire hazard with the corresponding marking PVSng-LS:
- ng in the marking defines a non-combustible type of insulation;
- LS - indicates that insulation with reduced smoke emission during combustion is used.
Sometimes the abbreviation PVS can be confused with the consonant - PPP, but apart from the similar sounding of the names, these cables are nothing like each other. High voltage electricians know well what a PPS wire is - according to its technical characteristics, this wire is designed for transposition of cable screens and the cross section of the smallest of them is 70 mm². They are used by the relay protection service of distribution substations and such wires do not intersect with household needs.
Briefly about the main
The PVA cable has a fairly wide range of uses and the corresponding technical characteristics. Perhaps its only drawback is its relatively short service life - 5-10 years, which is why it is not recommended for use as a hidden wiring. Otherwise, the limitation on its use is imposed solely by the conductor cross-section and voltage.