What is grounding in the outlet for and how to check it
High voltage protection is an integral part of the electrical network and is performed in various ways, one of which is grounding. According to the rules of the PUE, it is an obligatory component, but in many houses, especially old buildings, it is still absent. To understand if there is such protection in your apartment, you need to know how to check the grounding in the outlet, because there are contacts for it in all modern electrical appliances.
Content
Why ground an electrical circuit

Many ordinary people are driven into a stupor by the information that the zero and the grounding conductor in the socket can be planted on the same wire on the floor panel (or the main distribution panel of the house). A natural question arises - why pull the third wire, if two of them are still closed with each other?
In practice, a fundamental principle is applied here - everything in nature moves along the path of least resistance from greater to less. Water flows from top to bottom, heat is transferred from a hot body to a cold one, and an electric current flows to where the resistance of the conductors is lower.
If a short circuit occurs in an electrical circuit without grounding, then its mechanism of action is approximately as follows:
- The strength of the current and voltage in the network suddenly increases tens of times.
- If the wiring is weak, it will burn out.
- If the conductor of the wiring is of sufficient thickness (section) to withstand the increased loads, then it heats up, from which the insulation ignites.
- Whether the wiring is burnt out or not, but if during a short circuit a person touches any metal part of the device, then he gets an electric shock, and its values are an order of magnitude higher than just in the outlet. In the first case, this is a short-term blow, and in the second, until the current finds the weak point of the wiring and burns it, after which the circuit is opened.
If there is grounding, then everything is not so sad:
- The current and voltage increase, but at the same time they immediately have "where to run" - the ground wire.
- The natural resistance of the human body is much greater than that of copper, aluminum or steel, so even if a person holds onto the metal parts of the device, the current will simply "pass by" along an easier path. Hence, one of the requirements for the grounding wiring - it should be performed, if possible, with one solid wire - twists are allowed on the floor panel, on the input machine, and one solid core goes on through the apartment.
On ordinary wiring, there are circuit breakers that operate if the load in the circuit exceeds the permissible limits. On the grounding wire, during normal operation of the circuit, there should be no voltage at all, therefore, in conjunction with it, it is logical to use an RCD that reacts to the leakage current, which is usually insignificant. As a result, in case of a short circuit, the current turns off immediately, and not due to the melting of the wiring.
For more information on what happens when a short circuit occurs in the circuit, see this video:
The above describes the role of grounding in terms of electrical safety, but it also serves to prevent electrical noise that can negatively affect the operation of computers and other delicate devices. See this video for more details:
Household methods for checking the presence of grounding
If it is clear why you need grounding in the outlet, then the question remains how to find out if it works - after all, in practice, zero in the network is always grounded and, in fact, the connection goes along the same wire.Here you need to understand that in some cases, grounding is an additional zero, but with as little wire resistance as possible. It should also be borne in mind that the wiring in the apartment can be done correctly, but if there are no separate grounding terminals on the driveway, the wire can be left unconnected until a separate grounding bus is installed in the house.
For the simplest check you need voltage indicator or tester, control light and screwdriver.
Visual inspection

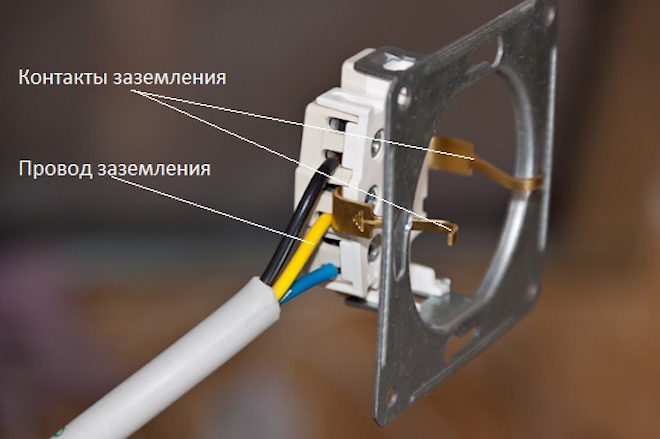
The first step is to look at the design of the sockets in the house - they can only have two holes for a plug or with additional contacts.
In the first case, it is clear that the design of the sockets themselves does not provide for the presence of grounding. In the second, it is possible to connect protection to them in principle, but whether it actually exists, it is necessary to check additionally.
Then the socket itself is disassembled - here you need to look at how many wires come out of the wall and what color they are. According to the standards, the phase is connected with a brown (black, gray, white) wire, zero blue, and a two-color yellow-green ground. In older homes, this can be just a two- or three-core single-color wire. If only two wires are used, then this clearly indicates the lack of grounding. If three cores come out, then additional verification will be required.
Additionally, you need to inspect the shield near the electricity meter - if only two wires enter the apartment, this also indicates that there is no grounding initially.
Zeroing in the absence of grounding
It is possible to find only two wires entering the apartment, but at the same time, when examining the outlets, it is clear that the contacts for grounding and the neutral wire are shorted together with a jumper. This connection option is called grounding, but it is forbidden to use it by the rules of the PUE, since in case of a short circuit, the voltage immediately appears on the instrument cases and there is a high probability of electric shock to a person.
Even without a short circuit, such a connection is dangerous with a fairly common breakdown - a burnout of the neutral wire on the input machine. In this case, the phase through the contacts of the devices turns out to be on the neutral wire, which, after burnout, is not connected to ground. The voltage indicator will show the phase in all contacts of the outlets.
About what zeroing is and how dangerous it is, see this video:
How to determine the presence of grounding
If there are three wires to the outlet and all of them are connected to it, you can check the efficiency of the grounding with a tester or an ordinary light bulb.
To do this, it is necessary to determine on which wire the phase sits, which is done by the voltage indicator. Moreover, if a phase is detected on two wires, then the network is faulty.
When the phase is found, one wire of the light bulb is touched to it, and the second is alternately touched to zero and ground. When you touch the neutral wire, the light should light up, but if there is grounding, you need to look at its behavior - the following options are possible:
- The light is off. This means that there is no grounding - most likely, the wire is not connected anywhere in the switchboard.
- The light is on in the same way as when connected to the neutral wire. This means that there is grounding, and in the event of a short circuit, the current will have where to go, but there is no protection that is triggered by the leakage current.
- The light starts to glow (in some cases it does not have time to light up), but then the electricity is turned off in the whole apartment. This means that the grounding is connected and working correctly - there is an RCD machine on the input panel of the apartment, which cuts off the voltage when a leakage current occurs, which goes to the grounding wire.
When checking, you need to pay attention to the brightness of the light bulb or what values the voltmeter shows.If, compared to the connection to the neutral wire, the light is dimmer (or the voltage is less), then the resistance of the ground wire is higher and its efficiency is low.
Complete grounding check
In fact, even the presence of grounding in an apartment does not yet guarantee its correct operation. For a complete check, it is necessary to carry out a series of measurements of the resistance of the conductors to make sure that the ground wire is indeed a "convenient" path for the electric current and, in the event of a short circuit, it will flow in the right direction.
It is almost impossible to carry out such a check at home, since it requires sensitive devices. In addition, it is necessary to measure the resistance of the conductors not only in relation to each other, but also to the ground. If you're curious about how it's done, take a look here:
As a result, if grounding is needed not only to protect a person from electric shock, but also to clean sensitive devices (for example, in a sound recording), it is advisable to contact a specialist for verification. Otherwise, it is enough that when a leakage current appears on the grounding conductor, the RCD protective circuit breaker is triggered.




