How to choose the right RCD for an apartment or a private house?

The purpose of the RCD has already been repeatedly mentioned, and clearly its installation in a modern household electrical network is the most important protection of a person from electric shock. But how to choose an RCD? Based on what parameters? How to calculate the device for a particular protected consumer? Let's try to figure it out.
To make the right choice of an RCD, you need to understand its purpose, main characteristics and parameters. When you buy a device, pay attention to its case, it contains all the important information. So that these numbers and letters tell you something, we will analyze each of them separately.
Content
Appointment
The most important thing to understand is that the circuit breaker protects the electrical network from overcurrents, and the RCD protects the person. If, as a result of insulation breakdown, a potential appears on the body of the electrical appliance, when you touch it, there is a possibility of getting an electric shock. To prevent this from happening, immediately when a leakage current occurs, the residual current device will react and disconnect the damaged section of the circuit.
It's important to know! The RCD does not protect against overloads and short circuits, therefore, circuit breakers must be connected in series with them in the circuit.

Trademark
Speaking of the brand, we are, in essence, going to analyze the value for money. The fact is that there is an unspoken classification of all RCD manufacturers according to their territorial location - European models, Asian and Russian.
One way to spot a fake video:
Each of them has its own specific features:
- Both a fire-prevention RCD and a device that protects people from electric shock, produced in Europe, will cost an order of magnitude more expensive than models in Russia and China. But this price guarantees quality and reliability. It will not be superfluous to know that some European companies, in addition to the main high-quality assortment, produce RCDs for the markets of other countries with the same reliability, but with underestimated technical characteristics.
- Domestic manufacturers offer RCDs with a lower price than analogs from Europe, however, they meet all the regulatory requirements of Russian standards. So far, the retail network of Russian manufacturers is not so strong, and the devices themselves are not able to compete with Asians in terms of price, with Europe in terms of quality.

- RCDs of Asian manufacturers are in the greatest demand in the world. Some manufacturers from Asia enter into contracts with a supplier of products to the Russian market, and in this case they release devices under the Russian trademark.
Before choosing a RCD trademark, decide what means you have at your disposal for equipping an apartment or in a private house of protective automation. Most preferred firms:
- Swiss "ABB";
- French "Legrand" and "Schneider Electric";
- German "Siemens" and "Moeller".
Among domestic manufacturers, the most widely used products are:
- Kursk plant "KEAZ", the average price and quality, the company gives a two-year guarantee for the manufactured RCDs, which indicates the reliability of the products;
- The Moscow firm "Interelektrokomplekt" ("IEK"), the products do not always receive positive reviews, nevertheless, the demand for it is great due to the low cost;
- Ulyanovsk plant "Kontaktor", it is part of the group of companies "Legrand", which affects the quality of products and, accordingly, the price;
- a relatively young St. Petersburg firm "DEKraft", on the Russian market it represents the world-renowned company "Schneider Electric".

As for the Chinese manufacturers, the RCDs they produce are a direct competitor to the devices of the Russian company IEK. Price and quality are approximately at the same level, while the warranty period for the Chinese product is five years.
main parameters
After the trademark on the case, the main ratings and operating characteristics of the RCD are indicated.
- Model name and series. Please note that here you will not always see the letters RCD, some manufacturers designate this device as a RCD (residual current switch).
- The magnitude of the rated voltage and frequency. In the Russian power system, the operating frequency is 50 Hz. As for the voltage, for a single-phase network in an apartment it is 220-230 V. For a private house, a three-phase network is sometimes needed and the operating voltage will be 380 V.
RCD characteristics in the video:
- The rated operating current is the maximum value that the RCD can switch.
- Rated differential breaking current. This is the amount at which the device is triggered.
- Also, the temperature limits of the RCD operation are indicated here (minimum - 25 degrees, maximum + 40).

- Another current value is the rated conditional short-circuit current. This is the maximum short-circuit current that the device will withstand and not turn off, but provided that a suitable automatic machine is installed in the circuit in series with it.
- Rated response time. This is the time interval from the moment when the current leakage suddenly occurred and before it should be extinguished by all poles of the RCD. The maximum permissible value is 0.03 s.
- Be sure to draw an RCD diagram on the case.
Leakage current shape
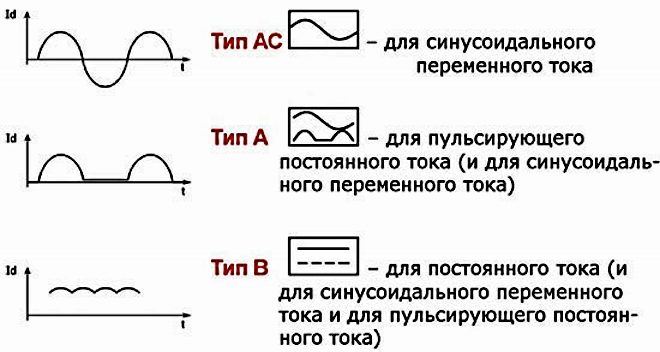
For this parameter, all residual current devices are classified into three types:
- "AND". Such a device operates to trip when instantly occurring or gradually increasing current leaks, having a sinusoidal variable or pulsating constant shape. This is the most common type of RCD. Due to the fact that it controls both AC and DC currents, it is more expensive.
- "AC". Also a common and more affordable device. Works only on the occurrence of alternating sinusoidal current leakage.
- "IN". This device is mainly used to protect industrial premises. In addition to the variable sinusoidal, the RCD responds to the rectified and pulsating form of constant current leakage.
A completely logical question arises, an alternating current of a sinusoidal form flows in household networks, can it be enough to install devices of the "AC" type everywhere? But if you take a closer look at the characteristics of modern household appliances, then most of them have power supplies with electronic semiconductor components, reaching which the sinusoid is converted into pulse half-periods. And if the leak is not sinusoidal, then the RCD of the "AC" type will not fix it and will not turn off.
That is why, in the passports for many household appliances, the manufacturer indicates through which RCD it is necessary to connect.
Tips for choosing an RCD in the video:
Operating principle
There are electronic and electromechanical RCDs.
The second is more expensive, but does not depend on the supply network. It will work as soon as a current leak occurs in the circuit.
An electronic device in its operation depends on an amplifier built into the electrical circuit. And for this amplifier to always be in working order, it needs an external power supply. In this regard, the reliability of the actuation is reduced.
When choosing an RCD for this parameter, we advise you to give preference to electromechanical devices.
Selectivity
According to the selectivity of operation, residual current devices are of two types - "G" and "S".
These RCDs operate after a certain period of time, called a delay.They are used when several devices are connected in series in a chain. To protect the outgoing consumer branches, devices are installed without time delay, and at the input of RCDs of type "G" and "S". If there is a current leakage, and the outgoing RCD has not responded, then after a certain time the device at the input should turn off.
For "S" type RCDs, the shutter speed is adjusted in the range from 0.15 to 0.5 s, for type "G" - from 0.06 to 0.08 s.
Two-level fire protection
For a wooden private house, the guarantee of fire safety is especially important. Therefore, in this situation, it is necessary to select an RCD when planning a two-level differential protection system. Its main purpose is to separate the protective function:
- fire-fighting RCD provides operation in case of large current leaks, contributing to a fire;
- Ordinary devices will prevent electric shock to humans at low leak rates.
Since a fire-fighting RCD has a great value for the rated leakage current, it alone will not provide protection to a person. Therefore, it is always installed in conjunction with an RCD, which has a lower leakage current.
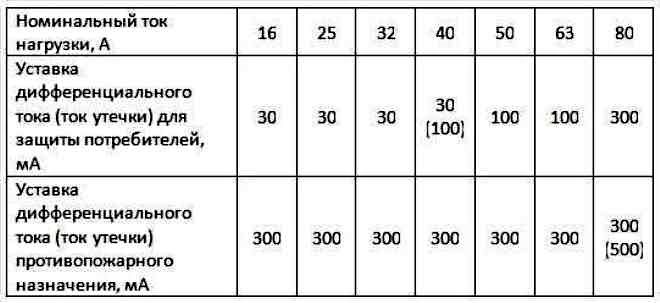
Regardless of what value is the rated operating current and how many poles a fire-fighting RCD has, the leakage current parameter of such a device is 100 mA and 300 mA, otherwise it is no different from an ordinary one.
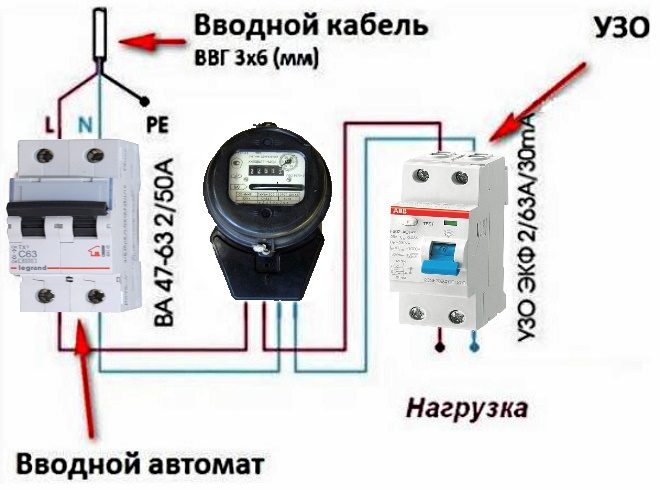
The connection diagram is performed in series, closer to the power source (at the input) we put a fire-prevention RCD, and on the outgoing branches of the protected wiring, universal.
Clearly about the fire-prevention RCD in the video:
For example, it looks like this: the input RCD is selected with the parameters 63 A (rated operating current) and 300 mA (leakage current), the other devices, respectively, 40 A and 30 mA for the outlet group, 25 A and 10 mA for the bathroom, 16 A and 10 mA for the lighting group.
The use of fire-fighting devices is also advisable in the apartment. Often the lighting group is left unprotected against leakage currents. With a minimum probability, but high current leakages can occur in this branch as well, and if such an RCD is installed at the input, it will be a kind of safety net.
Performing calculations
Let's try, using an example, to calculate which RCD you still need to choose for a particular protected branch of electrical home wiring.
In practice, it is not always possible to accurately calculate the total leakage current. Therefore, approximately it is determined by the following method: for 1 A of the consumed load, 0.4 mA of current leakage is taken. You should also make a calculation based on the length of the phase wire - 10 μA is taken for 1 m.
Let's say you need to choose the right RCD according to the power of the electric stove (3 kW). To begin with, we calculate its load: 3000 W / 220 V = 13.64 A. Leakage current for the plate: 13.64 A x 0.4 mA = 5.46 mA. Similarly, we make a calculation for a laid conductor, for example, 10 m: 10 μA x 10 m = 100 μA = 0.1 mA. In total, the leakage current is 5.46 mA + 0.1 mA = 5.56 mA.
The resulting value of the sum of the current leakage should not exceed 33% of the differential rated current of the RCD. And then the calculation from school math lessons, we make up an elementary proportion and get: 5.56 mA x 100% / 33% = 16.85 mA.
There is a special table of standard values of rated leakage currents, based on it, a 25 mA device is suitable for an electric stove.
You now know how to choose an RCD for an apartment or house, and you will be able to determine the total calculated leakage current yourself. If you have any doubts about your knowledge and abilities, invite a professional electrician to do the job. Remember that the residual current device is your guarantee of your safety.